| Info | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
1006.06.20212022 Re-open EU provides information on the various measures in place, including on quarantine and testing requirements for travellers, the EU Digital COVID certificate to help you exercise your right to free movement, and mobile coronavirus contact tracing and warning apps. The information is updated frequently and available in 24 languages. This should help you plan your travel in Europe, while staying safe and healthy. Information for travellers from third countries to the EU From 3 June, the revised list of third countries for which travel restrictions should be lifted consists of the following:
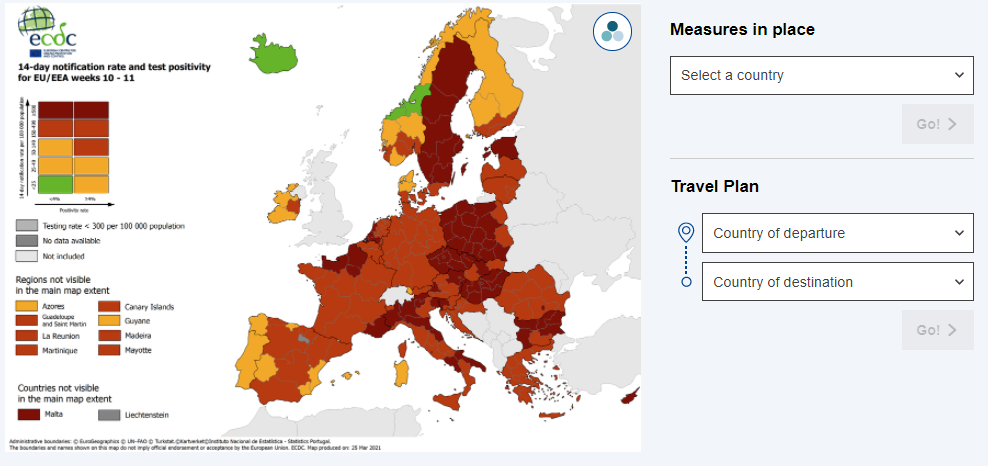
EU countries have agreed on a revised coordinated approach to the restriction of free movement in response to the coronavirus pandemic. This is now based on the individual situation of travellers - whether or not they hold a valid 'EU Digital COVID Certificate'. The colour-coded map shows the epidemiological situation of EU regions. Note: EU countries are expected to apply measures to discourage non-essential travel from dark red areas. They can also implement further restrictions on free movement to protect public health. Travelling from outside the EU A temporary restriction on non-essential travel to the EU is currently in place from many non-EU countries. The EU has created a list of countries for which these restrictions should be lifted. This list is reviewed every two weeks. It was last updated on 17 January 2022, and includes:
Travel restrictions should also be gradually lifted for the special administrative regions of China:
Under the category of entities and territorial authorities that are not recognised as states by at least one EU Member State, travel restrictions for Taiwan should also be gradually lifted. Residents of Andorra, Monaco, San Marino and the Vatican should be considered as EU residents in this context. As of 1 March 2022, EU countries should allow non-essential travel also for the purpose of this recommendation.
01.04.2021 Travel Plan toolSource: https://reopen.europa.eu/en/from-to/*/ 18.12.2020 EU-UK relations: parliament adopts temporary contingency measuresOn Friday, Parliament adopted measures to ensure basic road and air connections in case no agreement is reached on EU-UK future relations.
Background EU rules will no longer apply to and in the UK after the end of the transition period. The targeted contingency measures aim to avoid serious traffic disruptions and considerable delays in case there is no agreement on EU-UK future relations in place by 1 January 2021. The contingency measures will cease to apply, if an agreement is reached. MEPs also approved the Commission’s proposal to extend reciprocal access by EU and UK vessels to each other’s waters until 31 December 2021 by 677 votes in favour, 4 against and 6 abstentions. Read more here. Next steps All temporary rules have to be adopted by the Council. They will enter into force after publication in the EU Official Journal and become applicable if a similar set of measures is adopted by the UK.
12.11.2020 EU countries have agreed on a coordinated approach to the restriction of free movement in response to the coronavirus pandemic. This includes a colour code for the classifications of regions - green, orange, yellow and grey - based on the epidemiological situation there. They also agreed on common criteria that they should apply when deciding whether to introduce travel restrictions, a common approach for travelers from ‘red areas’ (testing and self-quarantine), as well as on providing more clear and timely information to the public. This website will gradually provide more information as it becomes available. Information for travellers from third countries to the EU The Council updated the list of countries for which travel restrictions should be lifted. This list will continue to be reviewed and, as the case may be, updated every two weeks. Based on the criteria and conditions set out in the recommendation, member states should gradually lift the travel restrictions at the external borders for residents of the following third countries:
Travel restrictions should also be gradually lifted for the special administrative regions of China Hong Kong and Macao, subject to confirmation of reciprocity. Residents of Andorra, Monaco, San Marino and the Vatican should be considered as EU residents for the purpose of this recommendation. Source : https://reopen.europa.eu/en | ||||
| Info | ||||
|
| View file | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
English DownloadPDF
30.06.2020
Temporary Restriction on Non-Essential Travel to the EU
The Council adopted on 30 June, a Recommendation on the gradual lifting of the temporary restrictions on non-essential travel into the EU. Travel restrictions should be lifted for countries listed in the recommendation (consult the website). Upon revision by Member States and the Council, this list will be reviewed every two weeks.
Start date: 01.07.2020
Further information: https://ec.europa.eu/info/live-work-travel-eu/health/coronav...
More info: https://ec.europa.eu/info/live-work-travel-eu/health/coronavirus-respo...
Source: https://ec.europa.eu/transport/coronavirus-response_en
Travel restrictions
On 17 March 2020, EU Member States agreed on coordinated action at the external borders based on the recommendation by the Commission to restrict non-essential travel for an initial period of 30 days. This was prolonged several times until 30 June 2020.On 11 June 2020, the Commission adopted a Communication which set out an approach to progressively lift the restriction afterwards.
On 25 June, the Commission adopted a draft proposal for a Council Recommendation indicating that travel restriction should be lifted for countries selected together by Member States, on the basis of a set of principles and objective criteria including the health situation, the ability to apply containment measures during travel, and reciprocity considerations, taking into account data from relevant sources such as ECDC and WHO. Based on this approach, the Council adopted on 30 June, a Recommendation on the gradual lifting of the temporary restrictions on non-essential travel into the EU. Travel restrictions should be lifted for countries listed in the recommendation. Upon revision by Member States and the Council, this list will be reviewed every two weeks.
Based on the criteria and conditions set out in the Recommendation, as from 1 July Member States should start lifting the travel restrictions at the external borders for residents of the following third countries:
- Algeria
- Australia
- Canada
- Georgia
- Japan
- Montenegro
- Morocco
- New Zealand
- Rwanda
- Serbia
- South Korea
- Thailand
- Tunisia
- Uruguay
- China, subject to confirmation of reciprocity
Residents of Andorra, Monaco, San Marino and the Vatican should be considered as EU residents for the purpose of this recommendation.
While the restrictions on non-essential travel and their lifting depend on the traveller’s place of residence, the visa requirement continues to depend on nationality. If a traveller resides in a country where restrictions have been lifted, but is a national of a visa-required country, he or she must apply at the consulate of the Member State to which he wishes to travel to, in his or her country of residence.
For all other third countries not on this list, Member States and Schengen Associated countries are temporarily suspending all non-essential travel from those third countries to the EU+ area, meaning that only certain categories of travellers could be authorised entry. The “EU+ area” includes 30 countries: 26 out of the 27 EU Member States as well as the four Schengen Associated States: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. Ireland does not currently apply the travel restriction.
Travel restrictions aim to reduce the number of travellers entering the European Union. The aim is to restrict the spread of the coronavirus and protect public health within the EU, as well as to prevent the virus from spreading from the EU to other countries.
As the epidemiological situation in and outside the EU evolves and travel restrictions at the EU’s external borders gradually start to be lifted, visa operations will also resume gradually. On 11 June 2020, the Commission published a Guidance for a phased and coordinated resumption of visa operations.
The rules for applying for a short-stay visa remain unchanged. Member States’ consulates and external service providers will, however, have adapted practical aspects of access management, hygiene measures, payment methods etc. Applicants are advised to verify websites for information of the procedure to follow in advance.
Information on travel restrictions in place should be available on the websites of the relevant national authorities (e.g. Ministries of Interior and Foreign Affairs). A daily summary of flight and passenger restrictions is available on the Eurocontrol website and is entitled ‘Covid Notam (notice to airmen) summary’.
Exemptions from travel restrictions
The following categories of persons are exempt from the temporary travel restriction to the EU+ area from the third countries which are not on the list agreed by the Member States:
(a) Union citizens within the meaning of Article 20(1) TFEU and third-country nationals who, under agreements between the Union and its Member States, on the one hand, and those third countries, on the other hand, enjoy rights of free movement equivalent to those of Union citizens, as well as their respective family members.
(b) third-country nationals who are long-term residents under the Long-term Residence Directive or deriving their right to reside from other EU Directives or national law or who hold national long-term visas, as well as their respective family members.
The temporary travel restrictions should also not apply to people with an essential function or need, including
- healthcare professionals, health researchers, and elderly care professionals
- frontier workers
- seasonal workers in agriculture
- transport personnel
- Diplomats, staff of international organisations and people invited by international organisations whose physical presence is required for the well-functioning of these organisations, military personnel and humanitarian aid workers and civil protection personnel in the exercise of their functions;
- passengers in transit
- passengers travelling for imperative family reasons
- seafarers
- persons in need of international protection or for other humanitarian reasons;
- third-country nationals travelling for the purpose of study;
- highly qualified third-country workers if their employment is necessary from an economic perspective and the work cannot be postponed or performed abroad.
Exemption details
Seasonal workers
Temporary travel restrictions should not apply to travel by people with an essential function or need, including seasonal workers in agriculture.
Medical professionals
Temporary travel restrictions should not apply to travelling by people with an essential function or need, including healthcare professionals, health researchers, and elderly care professionals.
EU citizens’ family members*
The temporary travel restriction must exempt nationals of all EU Member States and Schengen Associated States, as well as their family members.
*Family members (as defined in Articles 2(2) and 3(2) of Directive 2004/38/EC):
Articles 2(2):
(a) the spouse;
(b) the partner with whom the Union citizen has contracted a registered partnership, on the basis of the legislation of a Member State, if the legislation of the host Member State treats registered partnerships as equivalent to marriage and in accordance with the conditions laid down in the relevant legislation of the host Member State;
(c) the direct descendants who are under the age of 21 or are dependants and those of the spouse or partner as defined in point (b);
(d) the dependent direct relatives in the ascending line and those of the spouse or partner as defined in point (b);
Articles 3(2):
(a) any other family members, irrespective of their nationality, not falling under the definition in point 2 of Article 2 who, in the country from which they have come, are dependants or members of the household of the Union citizen having the primary right of residence, or where serious health grounds strictly require the personal care of the family member by the Union citizen;
(b) the partner with whom the Union citizen has a durable relationship, duly attested.
Transport personnel
The temporary travel restrictions should not apply to transport personnel. This category should be interpreted broadly.
Someone claiming asylum
The temporary travel restrictions should not apply to travel by people with an essential need, including persons in need of international protection or for other humanitarian reasons.
Third-country students
This new exception covers third-country students starting or continuing their studies in the EU in the academic year 2020/21. A student is defined in Article 3(3) of the EUs Students and Researchers Directive 2016/801 as “a third-country national who has been accepted by a higher education institution and is admitted to the territory of a Member State to pursue as a main activity a full-time course of study leading to a higher education qualification recognised by that Member State, including diplomas, certificates or doctoral degrees in a higher education institution, which may cover a preparatory course prior to such education, in accordance with national law, or compulsory training.”
Third-country workers
This new exception covers third-country workers who, because of their high level of skills and knowledge, are needed to contribute to the EU’s post-COVID economic recovery. It may include those whose application for permits under the EUs Blue Card Directive 2009/50, the EU ICT Directive 2014/66, the Directive 2016/801 as Researchers, or under a national scheme for skilled migrants was approved, but who were until now prevented from entering the EU due to the entry ban.
Further information
Schengen visa holders currently in the EU
Visa holders present in the Schengen area who cannot leave at the expiry of their short-stay visa must contact the authorities of the Member State in which they are located to ask for an extension of their visa. A visa may generally be extended to allow for a total stay of 90 days in a 180 days period.
List of relevant national authorities in Member States
Nationals of visa-waived third countries who have remained in the Schengen area beyond the permitted 90-day stay
For nationals of visa-waived third-countries who are compelled to stay beyond the extended 90/180 days, the competent national authorities should extend the validity of the authorisations for legal stay, issue a new one or take other appropriate measures ensuring a continued right to stay on their territory. Information is available on the websites of Member States’ national authorities.
Irish citizens (and residents)
Although Ireland is not part of the Schengen area, all EU citizens and their family members must be exempt from the temporary travel restriction.
United Kingdom citizens
UK nationals are still to be treated in the same way as EU citizens until the end of the Brexit transition period (31.12.2020). Therefore, during that time UK nationals and their family members are exempt from the temporary travel restriction.
Transit through other EU Member States (road transit or transfer at airport)
EU citizens who are returning to their Member State of nationality or residence, as well as their family members, irrespective of their nationality, should be allowed onward transit. Given the reduced availability of commercial flights, ‘onward transit’ should cover any means of transportation.
EU citizens returning to their Member State of nationality or residence from a third country
The temporary restrictions on non-essential travel to the EU do not apply to returning EU citizens and citizens of the Schengen Associated States.
Expired travel documents due to an unexpectedly extended stay abroad
EU citizens and their family members who are not in possession of a valid passport and/or visa should be allowed to enter the EU territory, if they can prove by other means that they are EU citizens or family members of an EU citizen. Possession of an expired passport should be deemed to constitute proof by other means in the current situation. Family members should always be able to prove that they are indeed family members of the EU citizen.
Transit through airports located in an EU Member State or Schengen Associated States
Passengers travelling from a non-EU country to another non-EU country may transit through the international transit area of airports located in the Schengen area. Rules regarding airport transit visa requirements continue to apply.
Temporary Restriction on Non-Essential Travel to the EU (17.03.2020)
EU Leaders agreed to temporary restriction of non-essential travel from third countries into the EU area for 30 days. Any possible prolongation of this period should be assessed depending on further developments. The temporary travel restriction foresees exemptions for nationals of all EU Member States and Schengen Associated States (Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland; whilst UK nationals are still to be treated in the same way as EU citizens until end 2020), for the purposes of returning to their homes. Exceptions are also foreseen for travellers with an essential function or need.
Start date: 17.03.2020
End date: 30 days from starting date
Further information: https://eeas.europa.eu/headquarters/headquarters-homepage_en
persons vaccinated with vaccines approved by the EU or by the World Health Organization and for persons who recovered from COVID-19.
Background:
On 30 June 2020, the Council adopted a recommendation on the possible gradual lifting of the temporary restrictions on non-essential travel into the EU. In its 'Annex I', the recommendation includes a list of countries, special administrative regions and other entities and territorial authorities for which travel restrictions should be lifted. This list is reviewed every two weeks and, where appropriate, updated.
According to the recommendation, vaccinated persons, essential travellers and non-essential travellers from countries or entities included on Annex I should be allowed to travel into the EU under certain conditions.
Non-essential travel to the EU from countries or entities not listed in Annex I is temporarily restricted. However, EU countries can lift the temporary restriction on non-essential travel to the EU for fully vaccinated travellers.
Schengen associated countries (Iceland, Lichtenstein, Norway, Switzerland) also take part in this recommendation.
___________________________________________________________________________
26.11.2021
Temporary emergency travel restrictions into the EU
On 26 November 2021, in response to the emergence of the new COVID-19 variant 'Omicron', EU countries decided to adopt an urgent, temporary restriction on all travel into the EU from the following countries:
- Botswana
- Eswatini
- Lesotho
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- South Africa
- Zimbabwe
This travel restriction, called 'emergency brake mechanism', involves suspending passenger flights from affected countries and discouraging travel to these countries for EU citizens. The emergency brake mechanism should not apply to EU citizens, long-term EU residents and certain categories of essential travellers, who should nevertheless be subject to appropriate testing and quarantine measures, even if fully vaccinated.
Non-essential travel into the EU
Every two weeks EU Member States review and, where appropriate, update the list of non-EU countries from which non-essential travellers should be allowed. This list was last updated on 2 December 2021, and includes:
- Argentina
- Australia
- Bahrain
- Canada
- Chile
- China (subject to confirmation of reciprocity)
- Colombia
- Indonesia
- Kuwait
- New Zealand
- Peru
- Qatar
- Rwanda
- Saudi Arabia
- South Korea
- United Arab Emirates
- Uruguay
Travel restrictions should also be gradually lifted for the special administrative regions of China Hong Kong and Macao.
Under the category of entities and territorial authorities that are not recognised as states by at least one EU Member State, travel restrictions for Taiwan should also be gradually lifted.
Residents of Andorra, Monaco, San Marino and the Vatican should be considered as EU residents in this context.
Schengen associated countries (Iceland, Lichtenstein, Norway, Switzerland) also take part in this recommendation.
Background:
On 30 June 2020, the Council adopted a recommendation on the possible gradual lifting of the temporary restrictions on non-essential travel into the EU. In its 'Annex I', the recommendation includes a list of countries, special administrative regions and other entities and territorial authorities for which travel restrictions should be lifted. This list is reviewed every two weeks and, where appropriate, updated.
According to the recommendation, vaccinated persons, essential travellers and non-essential travellers from countries or entities included on Annex I should be allowed to travel into the EU under certain conditions.
Non-essential travel to the EU from countries or entities not listed in Annex I is temporarily restricted. However, EU countries can lift the temporary restriction on non-essential travel to the EU for fully vaccinated travellers.
Overview of vaccines administered by third countries for which most EU Member States/EEA countries would waive travel restrictions
This document provides an overview of vaccines administered by third countries for which most EU Member States/EEA countries would waive travel restrictions. As such, this document also helps you determine if you can get an EU Digital Certificate in the EU after being vaccinated in a third country.
The information is provided by the EU Member States/EEA Countries in the EU Health Security Committee. As the situation may be evolving, it is advisable to contact the authorities of the concerned EU Member State/EEA Country to verify the situation with regard to the respective vaccines administered in third countries. The document may be periodically reviewed if new information from the EU Member States/EEA Countries becomes available.
Disclaimer: The information on this page is not exhaustive. It is based on the most recent available data provided by EU Member States and collected from other publicly available and authoritative national sources. While the Commission seeks to keep the information up to date, we take no responsibility of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness and accuracy of the information contained in this page or individual decisions based thereon.
Re-open EU uses eTranslation, the European Commission’s machine translation service, to provide rapidly updated content in all languages. While we strive to continuously improve user experience, machine translation may not always be 100% accurate.
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
10.06.2021
Re-open EU provides information on the various measures in place, including on quarantine and testing requirements for travellers, the EU Digital COVID certificate to help you exercise your right to free movement, and mobile coronavirus contact tracing and warning apps. The information is updated frequently and available in 24 languages. This should help you plan your travel in Europe, while staying safe and healthy.
Information for travellers from third countries to the EU
From 3 June, the revised list of third countries for which travel restrictions should be lifted consists of the following:
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Rwanda
- Singapore
- South Korea
- Thailand
- China, subject to confirmation of reciprocity
- Israel
- Japan
Travel restrictions should also be lifted for the special administrative regions of China Hong Kong and Macao, subject to confirmation of reciprocity.
Residents of Andorra, Monaco, San Marino and the Vatican should be considered as EU residents for the purpose of this recommendation.
EU Digital COVID Certificates
The EU Digital COVID Certificate (available from 1 July 2021) provides proof that a person has either:
- been vaccinated against COVID-19 (vaccine type and manufacturer, number of doses, date of vaccination);
- received a negative test result, PCR or rapid antigen, with the name of the test, date and time of test, test centre and result (self-tests are not valid);
- recovered from COVID-19.
When travelling, holders of the EU Digital COVID Certificate will have the same rights as citizens of the visited Member State who have been vaccinated, tested or recovered.
The certificate provides a standardised recognition of the holder's status related to vaccination, recovery from COVID or test result. Each country continues to be responsible for the definition of its own entry requirements and rules, which are not standardised at the EU level. This means that what you will be eligible for, upon presentation of this certificate, depends on the measures and entry rules in place at your country of destination.
How does it work:
- Member States issue a certificate automatically or upon request, which is issued either digitally or on paper, and has a QR code with an electronic signature;
- Citizens store the certificate in their digital app or wallet and can use it when they travel;
- When the verifier asks the citizen for the certificate, the QR code is shown and the digital signature is verified.
Find out more:
Information on the EU Digital COVID Certificate
Press Release
Questions & Answers
Factsheet
01.04.2021
Travel Plan tool
Source: https://reopen.europa.eu/en/from-to/*/
18.12.2020
EU-UK relations: parliament adopts temporary contingency measures
On Friday, Parliament adopted measures to ensure basic road and air connections in case no agreement is reached on EU-UK future relations.
- Basic air connectivity: the temporary rules ensuring certain air services between the UK and the EU continue for a maximum of six months were adopted with 680 votes in favour (3 against, 4 abstentions). This includes rights for UK and EU air carriers to continue to fly over and make technical stops on EU territory, as well as serve direct routes to the EU. Also a limited number of specific pandemic-related cargo flights will be allowed.
- Aviation safety: the regulation ensuring various certificates for products, parts, appliances and companies remain valid was adopted with 680 votes in favour (3 against, 4 abstentions). This will avoid UK and EU aircraft that use these products and services being grounded.
- Basic road connectivity: the temporary rules ensuring road freight and road passenger transport for a maximum of six months were adopted with 680 votes in favour (4 against, 3 abstentions). This will allow carriage of goods as well as coach and bus services coming to Europe and going to the UK to continue.
Background
EU rules will no longer apply to and in the UK after the end of the transition period. The targeted contingency measures aim to avoid serious traffic disruptions and considerable delays in case there is no agreement on EU-UK future relations in place by 1 January 2021. The contingency measures will cease to apply, if an agreement is reached.
MEPs also approved the Commission’s proposal to extend reciprocal access by EU and UK vessels to each other’s waters until 31 December 2021 by 677 votes in favour, 4 against and 6 abstentions. Read more here.
Next steps
All temporary rules have to be adopted by the Council. They will enter into force after publication in the EU Official Journal and become applicable if a similar set of measures is adopted by the UK.
12.11.2020
EU countries have agreed on a coordinated approach to the restriction of free movement in response to the coronavirus pandemic. This includes a colour code for the classifications of regions - green, orange, yellow and grey - based on the epidemiological situation there. They also agreed on common criteria that they should apply when deciding whether to introduce travel restrictions, a common approach for travelers from ‘red areas’ (testing and self-quarantine), as well as on providing more clear and timely information to the public.
This website will gradually provide more information as it becomes available.
Information for travellers from third countries to the EU
The Council updated the list of countries for which travel restrictions should be lifted. This list will continue to be reviewed and, as the case may be, updated every two weeks.
Based on the criteria and conditions set out in the recommendation, member states should gradually lift the travel restrictions at the external borders for residents of the following third countries:
- Australia
- Japan
- New Zealand
- Rwanda
- Singapore
- South Korea
- Thailand
- Uruguay
- China, subject to confirmation of reciprocity
Travel restrictions should also be gradually lifted for the special administrative regions of China Hong Kong and Macao, subject to confirmation of reciprocity.
Residents of Andorra, Monaco, San Marino and the Vatican should be considered as EU residents for the purpose of this recommendation.
Source : https://reopen.europa.eu/en
| Info | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
13.10.2020 A common approach to travel measuresOn 13 October, EU Member States adopted a Council Recommendation on a coordinated approach to the restriction of free movement in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. This Recommendation is based on the Commission’s proposal adopted on 4 September. A common approach to travel measures in the EU The Recommendation sets out four key areas where Member States will coordinate their efforts:
Factsheet - COVID-19 - A coordinated approach to the restriction of free movement
English DownloadPDF
30.06.2020 Temporary Restriction on Non-Essential Travel to the EU The Council adopted on 30 June, a Recommendation on the gradual lifting of the temporary restrictions on non-essential travel into the EU. Travel restrictions should be lifted for countries listed in the recommendation (consult the website). Upon revision by Member States and the Council, this list will be reviewed every two weeks. Start date: 01.07.2020 Further information: https://ec.europa.eu/info/live-work-travel-eu/health/coronav... More info: https://ec.europa.eu/info/live-work-travel-eu/health/coronavirus-respo... Source: https://ec.europa.eu/transport/coronavirus-response_en Travel restrictionsOn 17 March 2020, EU Member States agreed on coordinated action at the external borders based on the recommendation by the Commission to restrict non-essential travel for an initial period of 30 days. This was prolonged several times until 30 June 2020.On 11 June 2020, the Commission adopted a Communication which set out an approach to progressively lift the restriction afterwards. On 25 June, the Commission adopted a draft proposal for a Council Recommendation indicating that travel restriction should be lifted for countries selected together by Member States, on the basis of a set of principles and objective criteria including the health situation, the ability to apply containment measures during travel, and reciprocity considerations, taking into account data from relevant sources such as ECDC and WHO. Based on this approach, the Council adopted on 30 June, a Recommendation on the gradual lifting of the temporary restrictions on non-essential travel into the EU. Travel restrictions should be lifted for countries listed in the recommendation. Upon revision by Member States and the Council, this list will be reviewed every two weeks. Based on the criteria and conditions set out in the Recommendation, as from 1 July Member States should start lifting the travel restrictions at the external borders for residents of the following third countries:
Residents of Andorra, Monaco, San Marino and the Vatican should be considered as EU residents for the purpose of this recommendation. While the restrictions on non-essential travel and their lifting depend on the traveller’s place of residence, the visa requirement continues to depend on nationality. If a traveller resides in a country where restrictions have been lifted, but is a national of a visa-required country, he or she must apply at the consulate of the Member State to which he wishes to travel to, in his or her country of residence. For all other third countries not on this list, Member States and Schengen Associated countries are temporarily suspending all non-essential travel from those third countries to the EU+ area, meaning that only certain categories of travellers could be authorised entry. The “EU+ area” includes 30 countries: 26 out of the 27 EU Member States as well as the four Schengen Associated States: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. Ireland does not currently apply the travel restriction. Travel restrictions aim to reduce the number of travellers entering the European Union. The aim is to restrict the spread of the coronavirus and protect public health within the EU, as well as to prevent the virus from spreading from the EU to other countries. As the epidemiological situation in and outside the EU evolves and travel restrictions at the EU’s external borders gradually start to be lifted, visa operations will also resume gradually. On 11 June 2020, the Commission published a Guidance for a phased and coordinated resumption of visa operations. The rules for applying for a short-stay visa remain unchanged. Member States’ consulates and external service providers will, however, have adapted practical aspects of access management, hygiene measures, payment methods etc. Applicants are advised to verify websites for information of the procedure to follow in advance. Information on travel restrictions in place should be available on the websites of the relevant national authorities (e.g. Ministries of Interior and Foreign Affairs). A daily summary of flight and passenger restrictions is available on the Eurocontrol website and is entitled ‘Covid Notam (notice to airmen) summary’. Exemptions from travel restrictionsThe following categories of persons are exempt from the temporary travel restriction to the EU+ area from the third countries which are not on the list agreed by the Member States: (a) Union citizens within the meaning of Article 20(1) TFEU and third-country nationals who, under agreements between the Union and its Member States, on the one hand, and those third countries, on the other hand, enjoy rights of free movement equivalent to those of Union citizens, as well as their respective family members. (b) third-country nationals who are long-term residents under the Long-term Residence Directive or deriving their right to reside from other EU Directives or national law or who hold national long-term visas, as well as their respective family members. The temporary travel restrictions should also not apply to people with an essential function or need, including
Exemption detailsSeasonal workers Temporary travel restrictions should not apply to travel by people with an essential function or need, including seasonal workers in agriculture. Medical professionals Temporary travel restrictions should not apply to travelling by people with an essential function or need, including healthcare professionals, health researchers, and elderly care professionals. EU citizens’ family members* The temporary travel restriction must exempt nationals of all EU Member States and Schengen Associated States, as well as their family members. *Family members (as defined in Articles 2(2) and 3(2) of Directive 2004/38/EC): Articles 2(2): (a) the spouse; (b) the partner with whom the Union citizen has contracted a registered partnership, on the basis of the legislation of a Member State, if the legislation of the host Member State treats registered partnerships as equivalent to marriage and in accordance with the conditions laid down in the relevant legislation of the host Member State; (c) the direct descendants who are under the age of 21 or are dependants and those of the spouse or partner as defined in point (b); (d) the dependent direct relatives in the ascending line and those of the spouse or partner as defined in point (b); Articles 3(2): (a) any other family members, irrespective of their nationality, not falling under the definition in point 2 of Article 2 who, in the country from which they have come, are dependants or members of the household of the Union citizen having the primary right of residence, or where serious health grounds strictly require the personal care of the family member by the Union citizen; (b) the partner with whom the Union citizen has a durable relationship, duly attested. Transport personnel The temporary travel restrictions should not apply to transport personnel. This category should be interpreted broadly. Someone claiming asylum The temporary travel restrictions should not apply to travel by people with an essential need, including persons in need of international protection or for other humanitarian reasons. Third-country students This new exception covers third-country students starting or continuing their studies in the EU in the academic year 2020/21. A student is defined in Article 3(3) of the EUs Students and Researchers Directive 2016/801 as “a third-country national who has been accepted by a higher education institution and is admitted to the territory of a Member State to pursue as a main activity a full-time course of study leading to a higher education qualification recognised by that Member State, including diplomas, certificates or doctoral degrees in a higher education institution, which may cover a preparatory course prior to such education, in accordance with national law, or compulsory training.” Third-country workers This new exception covers third-country workers who, because of their high level of skills and knowledge, are needed to contribute to the EU’s post-COVID economic recovery. It may include those whose application for permits under the EUs Blue Card Directive 2009/50, the EU ICT Directive 2014/66, the Directive 2016/801 as Researchers, or under a national scheme for skilled migrants was approved, but who were until now prevented from entering the EU due to the entry ban. Further informationSchengen visa holders currently in the EU Visa holders present in the Schengen area who cannot leave at the expiry of their short-stay visa must contact the authorities of the Member State in which they are located to ask for an extension of their visa. A visa may generally be extended to allow for a total stay of 90 days in a 180 days period. Nationals of visa-waived third countries who have remained in the Schengen area beyond the permitted 90-day stay For nationals of visa-waived third-countries who are compelled to stay beyond the extended 90/180 days, the competent national authorities should extend the validity of the authorisations for legal stay, issue a new one or take other appropriate measures ensuring a continued right to stay on their territory. Information is available on the websites of Member States’ national authorities. Irish citizens (and residents) Although Ireland is not part of the Schengen area, all EU citizens and their family members must be exempt from the temporary travel restriction. United Kingdom citizens UK nationals are still to be treated in the same way as EU citizens until the end of the Brexit transition period (31.12.2020). Therefore, during that time UK nationals and their family members are exempt from the temporary travel restriction. Transit through other EU Member States (road transit or transfer at airport) EU citizens who are returning to their Member State of nationality or residence, as well as their family members, irrespective of their nationality, should be allowed onward transit. Given the reduced availability of commercial flights, ‘onward transit’ should cover any means of transportation. EU citizens returning to their Member State of nationality or residence from a third country The temporary restrictions on non-essential travel to the EU do not apply to returning EU citizens and citizens of the Schengen Associated States. Expired travel documents due to an unexpectedly extended stay abroad EU citizens and their family members who are not in possession of a valid passport and/or visa should be allowed to enter the EU territory, if they can prove by other means that they are EU citizens or family members of an EU citizen. Possession of an expired passport should be deemed to constitute proof by other means in the current situation. Family members should always be able to prove that they are indeed family members of the EU citizen. Transit through airports located in an EU Member State or Schengen Associated States Passengers travelling from a non-EU country to another non-EU country may transit through the international transit area of airports located in the Schengen area. Rules regarding airport transit visa requirements continue to apply. |
| Info |
|---|
Temporary Restriction on Non-Essential Travel to the EU (17.03.2020) EU Leaders agreed to temporary restriction of non-essential travel from third countries into the EU area for 30 days. Any possible prolongation of this period should be assessed depending on further developments. The temporary travel restriction foresees exemptions for nationals of all EU Member States and Schengen Associated States (Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland; whilst UK nationals are still to be treated in the same way as EU citizens until end 2020), for the purposes of returning to their homes. Exceptions are also foreseen for travellers with an essential function or need. Start date: 17.03.2020 End date: 30 days from starting date Further information: https://eeas.europa.eu/headquarters/headquarters-homepage_en |
| Note | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
12.10.2022 EU - BelarusBelarus: obtaining permits by EU carriers for travel through national territoryFrom 10 October road carriers of the European Union can obtain a permit for goods transport through the territory of Belarus. According to the information of the Ministry of Transport and Communications of the Republic of Belarus from 10 October 2022, road haulage carriers registered in Member States of the European Union can obtain the permit from the Transport Inspectorate for international road goods transport through the territory of Belarus. To do this, the carrier must:
The full procedure for carriers of the European Union, or their representative acting on the basis of a letter of attorney, for the registration of the permits for international road goods transport through the territory of Belarus in the Transport Inspectorate can be found at the following links: Additionally, the Ministry of Transport and Communications of Belarus clarified that the possibility introduced by the Belarusian side is valid simultaneously with the observance of the norms of the Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus from 22 April 2022 № 247 «On the movement of vehicles». Thus, in Belarus the rule for foreign carriers of delivery of goods for the purpose of subsequent reloading or recoupling in specially designated places in accordance with Decree No. 247 is retained. At the same time, the possibility and procedure for using permits for travel through the territory of Belarus, transferred by the Belarusian side to the competent authorities of foreign states, is also preserved. The translation in Russian is available for download when opening the Flash Info. Source: BAMAP, according to information from the Ministry of Transport and Communications of Belarus __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 04.07.2022 EU- Belarus / Russia Road transport operators continuing operations from the EU into Belarus, Russia and beyond into the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) are currently facing long waiting times at borders, with waiting times reaching one week or more. One reason for delays is insufficient customs guarantees from national providers who, in some cases, are unable to release their activated guarantees until the goods being transported have left EU territory. IRU reminds transport operators that the TIR system does not face this issue and is able to provide a seamless internationally recognised customs guarantee for transporting goods across these borders. TIR has high safety and security standards, and also therefore aids compliance with relevant trade sanctions on types of goods. Source: IRU, Latvijas and other IRU members __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 15.02.2022 European Commission letter to EU Member States on the application of the new rules on posting of drivers in the EUThe services of the European Commission sent the attached letter (available for download when opening the Flash Info post) to EU Member States on the application of the new EU rules on posting of drivers in the road transport sector. The letter makes clear that:
Source: European Commission ________________________________________________________________________ 10.01.2022 EU-UK: make sure the correct documents are available for customs checksFrom 1 January 2022, anyone moving goods between Great Britain (GB) and the European Union (EU) through a Goods Vehicle Movement Service (GVMS) border location must be registered to use this service. IRU has been informed that 30% of vehicles arriving at the French Channel crossings (ports and Eurotunnel) are presenting invalid Goods Vehicle References (GMRs). This causes additional waiting times and can lead to the vehicle being turned back or even being denied access to embarkation areas.
HMRC continues to undertake a wide variety of engagement activity with stakeholders to ensure they understand the new obligations and processes which will be in place. Additional useful information can also be found in the attached HMRC guidance note. Carriers are recommended to use transit procedure (such as TIR) in order to move the goods from / to UK, as using transit facilitates submission of information in GVMS. Sources: FNTR, Logistics UK, HMRC ________________________________________________________________________ 06.12.2021 COVID-19 Update testing exemption for vaccinated passenger coming from the European UnionPassengers who have been vaccinated arriving from the following countries do not need to get tested: any EU country, Andorra, Island, Liechtenstein, Monaco, Norway, San Marino, or Switzerland.
16.11.2021 Goods Vehicle Movement Service (GVMS) - Leaflet detailing new rules United Kingdom - European Union HMRC have just published leaflets for hauliers that move goods between the European Union and Great Britain (England, Scotland and Wales), explaining the new rules they need to follow from 1 January 2022, and how to prepare for these changes. The leaflet is available in 10 alternative languages in this link. Source: HMRC (UK Customs) ___________________________________________________________________________________ | ||||||
| Note | ||||||
| icon | false | title | Remarks from the International Road Transport UnionFrequently asked Questions on Testing Centres in EU IRU, with the help of our member associations, has put together a detailed list of Frequently asked Questions ( and their answers ) on the testing centres for non- established drivers in various countries in the European Union. Please find the document attached.
14.02.2021 Coronavirus (COVID 19) outbreak: The Austrian region Tyrol tightens access of goods transport drivers in transit to Germany in response to German measures Austria - European Union In response to the German measures, Tyrol already began to control and throttle truck traffic from Italy on Sunday in order to prevent a heavy traffic backlog and gridlock in the Inntal. Germany included the Czech Republic on the list of “new COVID-19 variant” countries, which implies that drivers of goods transport coming from the Czech Republic, including drivers just transiting the Czech Republic, will be demanded to present a negative test when entering Germany (for more information regarding the German measure see IRU Flash Info of 12 February). A regulation will be issued in coordination with the Austrian federal government that will enable controls to be carried out as soon as the Brenner Pass is reached and this will probably be published on Monday morning. Although officially not confirmed, it is believed that entry for the purpose of goods transport and transit will only be permitted if exit to Germany is guaranteed. There will be checks at the Brenner Pass to see if drivers have negative test results, otherwise entry will be refused. Test possibilities along the Austrian motorway network are not possible due to capacity reasons of the test stations but also of the parking areas. Source: AISO and Austrian press
01.01.2020 Change in operation of UK international bus and coach services in the EU United Kingdom - European Union Occasional passenger journeys by coach On 1 January 2021 the UK joined the Interbus Agreement, ensuring international bilateral (point-to-point) occasional (i.e. unscheduled) journeys to and from the EU to continue. Operators will not be able to transport passengers between two locations within the EU (known as cabotage), except as part of services between Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland. Interbus does not yet allow regular (scheduled) or special regular services. Regular and Special Regular services The UK-EU Free Trade Agreement will allow international bilateral (point-to-point) regular (i.e. scheduled) and special regular services to continue to operate. Operators will not be able to transport passengers between two locations within the EU (known as cabotage), except as part of services between Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland. Island of Ireland services Services operating between Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland will continue to operate with no changes. Operators will continue to be able to transport passengers between two locations within the Republic of Ireland as part of a service between Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland. Operators’ licences Regardless of what kind of international service you are running, from 1 January 2021 drivers will need to carry a certified true copy of their Operators’ Licence on board at all times. Certified copies are being sent to operators in the post automatically. Driver CPC Drivers will still need Driver CPC to drive professionally in the UK and the EU after Brexit. UK drivers must still complete their Driver CPC periodic training. Source: UK Driver and Vehicle Standards Agency 29.12.2020 EU-UK borders – Update of the situation in Kent United Kingdom - European Union FREIGHT HEADING TO KENT Source: RHA 28.12.2020 Brexit – update on permits and guarantees for customs United Kingdom - European Union According to the latest Brexit deal, unlimited bilateral transport will be possible, permits will not be needed as of 1.1.2021. For furnishing guarantees for customs duties and taxes, hauliers can use either CTC or TIR. The UK customs authorities (HMRC) have successfully tested TIR for transport between the EU and the UK and confirmed their readiness to continue handling it effectively as of 1 January 2021.
27.12.2020 Brexit – Coronavirus (COVID 19) outbreak: EU-UK borders – Update of the situation in Kent United Kingdom - European Union Our Member Association in the UK, the RHA, reports that the advice remains that hauliers must avoid traveling to Kent ports (including Eurotunnel) and other routes to France until further notice. Urgent work continues to resolve the matter. Unaccompanied freight will continue to be able to travel to France and inbound freight will still be allowed to come to the UK. Source: UK Road Haulage Association (RHA)
26.12.2020 Brexit - Draft EU-UK Trade and Cooperation Agreement published European Union - United Kingdom (26 December 2020) The European Commission has just published the full draft text of the EU-UK Brexit Trade and Cooperation Agreement, which can be downloaded at https://ec.europa.eu/info/files/eu-uk-trade-and-cooperation-agreement_en. The chapter on road transport (freight and passenger) starts on page 246. A formal approval is expected in the days to come on both sides, starting at EU side, by the Council, acting by the unanimity of all 27 Member States, adopting a decision authorising the signature of the Agreement and its provisional application as of 1 January 2021. For more information on the issue, please see https://ec.europa.eu/info/european-union-and-united-kingdom-forging-new-partnership/future-partnership/draft-eu-uk-trade-and-cooperation-agreement_en. The IRU Secretariat shall come up with an analysis in due course. Source: European Commission
25.12.2020 Brexit – Coronavirus (COVID 19) outbreak: European Commission overview of the temporary derogations in driving and rest time rules European Union (25 December 2020) The European Commission published an overview of the derogations/relaxations in enforcement of driving and rest time rules issued by several countries (attached). This info will also become available on the European Commission website: https://ec.europa.eu/transport/sites/transport/files/temporary-relaxation-drivers-covid.pdf
Source: European Commission Coronavirus (COVID 19) outbreak: European GNSS Agency - border situation monitoring application European Union The “Galileo Green Lane” mobile solution, developed in May by the European GNSS Agency (GSA) in collaboration with the European Commission helps to monitor the free movement of traffic across borders by providing a real-time visualisation of the border situation to both border authorities and drivers. Drivers can download and use this application to help facilitating their journey.. More information and a link to down load the application in the attached message from GSA (in English and in French).
Source: European GNSS Agency
02.10.2020 The European Commission has confirmed that from 2 February 2022 the new obligation to record manually border crossings, set out in Article 34(7) of the Tachograph Regulation, will also apply to drivers of vehicles equipped with an analogue tachograph. Drivers of vehicles equipped with an analogue tachograph do not need to manually record border crossings until 2 February 2022. This only applies to the obligation to record border crossings. The European Commission also confirmed that, as of 20 August 2020, drivers of vehicles fitted with analogue tachographs are required to record the symbol of the countries in which the daily working period started and finished. Source: European Commission
10.06.2020 Since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, the functioning of national authorities and the issuing of visas and residence permits has been impacted, resulting in a patchwork of different approaches by EU Member States. In order to provide more clarity on the different approaches, the European Commission (DG HOME) has recently published an overview of these different national practices regarding the extension of legal stay in the EU Member States as a result of COVID-19. The document provides the full text of notified information by the Member States, concrete legal impact of the measures, and a list of required documents for third country nationals. Moreover, the European Commission encourages EU Member States to consult the document and “not to consider as illegal stay in the EU the periods of stay in a Member State covered by the national measures listed therein.” Please access the document by clicking here. Source: European Commission
09.06.2020 On 8 June, the Official Journal of the EU published a list of Member States that have decided not to apply certain provisions of Regulation (EU) 2020/698, which lays down specific and temporary measures in view of the COVID‐19 outbreak concerning the renewal or extension of certain certificates, licences and authorisations, as well as the postponement of certain periodic checks and training in certain areas of transport legislation. The Member States involved are as follows: The above Member States are in addition to those on the list already published last week (France, Finland, Croatia, Lithuania, Poland, Latvia, Hungary, Estonia, Spain, United Kingdom, Ireland, Sweden, Cyprus, Greece, Romania, Luxembourg, Austria, Bulgaria, Malta, the Netherlands). Source: European Commission
08.06.2020 On 8 June, the Official Journal of the EU published a list of Member States that decided not to apply certain provisions of Regulation (EU) 2020/698, which lays down specific and temporary measures in view of the COVID‐19 outbreak concerning the renewal or extension of certain certificates, licences and authorisations, and the postponement of certain periodic checks and periodic training in certain areas of transport legislation. Member States involved are as following: These Member States are added to those whose notification was published on 2 and 3 June: Poland, Latvia, Hungary, Estonia, Spain, United Kingdom, Ireland, France, the Netherlands, Finland, Croatia, Lithuania. Source: European Commission
05.06.2020 On 3 June, the Official Journal of the EU published a list of Member States that decided not to apply certain provisions of Regulation (EU) 2020/698, which lays down specific and temporary measures in view of the COVID‐19 outbreak concerning the renewal or extension of certain certificates, licences and authorisations, and the postponement of certain periodic checks and periodic training in certain areas of transport legislation. Member States involved are as following: These Member States are added to those whose notification was published on 2 June: France, the Netherlands, Finland, Croatia, Lithuania. Source: European Commission
04.06.2020 On 2 June, the Official Journal of the EU published a list of Member States that decided not to apply certain provisions of Regulation (EU) 2020/698, which lays down specific and temporary measures in view of the COVID‐19 outbreak concerning the renewal or extension of certain certificates, licences and authorisations and the postponement of certain periodic checks and periodic training in certain areas of transport legislation. Member States involved are as following: Source: European Commission
28.05.2020 On 27 May, Regulation (EU) 2020/698 was published in the Official Journal of the EU. The Regulation lays down specific and temporary measures concerning the renewal or extension of certain certificates, licences and authorisation and the postponement of certain periodic checks and periodic training in the area of transport legislation. Concerning road transport, the following Regulations and Directives could be subject to temporary changes:
The Regulation enters into force on 4 June 2020. However, Article 3(4), Article 4(6), Article 5(5), Article 7(5), Article 8(5) and Article 11(5) apply from 28 May 2020. Source: European Union
20.04.2020 The European Commission services have updated the information on temporary relaxation of driving time and rest period. More information is also available on the dedicated section of EC website here. Source: European Commission, DG MOVE
12.04.2020 The European Commission services has just disseminated a note, advising EU Member States how to deal with driver cards under the current exceptional COVID-19 circumstances, where delays may be expected in issuing or replacing them. The EC recognises that the EU legislation, as contained in Regulation (EC) No 561/2006, Directive 2002/15/EC and Regulation (EU) No 165/2014 (Tachograph Regulation), does not contain a legal basis that would empower the Commission to authorise a derogation from the time limits contained in the legislation, to meet exceptional circumstances. However, in its capacity as guardian of the Treaties, the Commission is entitled to take account of exceptional circumstances to which Member States are exposed during the current crisis. The Commission services suggest, therefore, the below approach, provided that the measures adopted by EU Member States are limited to what is necessary in view of the current crisis, both in terms of substance and in time. - The national competent authorities should strive to supply a new card as soon as possible after the receipt of a detailed request to that effect. Under this approach, a deadline of 45 days after the receipt of the request could be considered reasonable under the current circumstances. - National enforcement authorities should take into account the current exceptional circumstances when performing controls of compliance with the Tachograph Regulation, to the extent that the driver has complied with his/her obligations. Regarding expired cards, the EC proposes the following approach: - The obligations set out in paragraphs 1 (obligation to apply for renewal 15 working days before the expiry date of the card) and 2 (provisions in case of renewals, in which the Member State of the driver’s normal residence is different from that which issued his/her current card) of Article 28 of the Tachograph Regulation apply. The submission of an online request is recommended and should be always preferred when available. - Without prejudice to the need for Member States to ensure that the relevant periods and events are properly recorded, the driver should always be in possession of the expired card and present it upon request of the control authorities. - The driver should keep the proof of the request of replacement of the expired card to the competent national authorities and present it to control authorities upon request. Source: European Commission
10.04.2020 Following many questions relating to issues with customs procedures during the COVID-19 crisis, the European Commission, DG TAXUD, established a webpage with guidance for economic operators regarding several customs issues. This information is regularly updated and therefore, should be consulted on a regular basis. The guidance includes aspects relating to customs decision-making, customs procedures and formalities. It covers issues on the use of NCTS and TIR, such as: - Empowerment of customs representatives for e-commerce - Prioritisation of essential customs decisions - Flexibility for customs debts and guarantees - Entry, transit and exit of goods - Customs and special customs procedures. Source: European Commission, DG TAXUD
09.04.2020 With regards to the various upcoming public holidays, Easter for example, please find below the updated decisions taken by the national authorities for the following countries vis-à-vis road transport activities. Details of the regulations normally applicable by country are available on IRU Information Centre. · Austria – on 6 April 2020, AISÖ confirmed that in Austria, the weekend and holiday driving ban for trucks over 7.5 tonnes will be suspended until 19 April 2020. However, members should be aware that the sectoral driving bans currently in place in the Tyrol region will remain valid. · Czech Republic – the applicable driving restrictions on Sundays and Public Holidays are lifted during the period of state emergency. · France – the applicable driving restrictions on weekends and Public Holidays are lifted until 20 April (further information of the normal applicable bans are available here). · Germany – the German Federal states’ exemptions on driving bans concern both Sunday and Public Holidays driving bans. The relevant exemptions granted in the Federal States are available here. · Greece – On 31 March, the Greek Ministry of Infrastructure and Transport decided to suspend traffic bans on the movement of trucks from 16 April until 21 April (Orthodox Easter). The suspension will also apply from 30 April until 3 May (weekend of Labour Day). · Italy - the Italian Minister of Transport and Infrastructure has signed a decree that lifts domestic traffic bans for goods vehicles heavier than 7.5 tonnes from 10 to 14 April. Holiday traffic bans for vehicles carrying out international transport in Italy are also lifted until further notice. · Portugal – During the Easter period, professional drivers must have a declaration signed by their employer attesting that the driver is performing a transport operation. The declaration aims at preventing the unnecessary movement of people during this Easter period. The form can be downloaded here. The obligation to carry such a document will come into force from 00:00 on 9 April, until 00:00 on 13 April. During this period, the movement of people will only be allowed for professional reasons (freight transport drivers included) or for specific needs (to go to hospital, pharmacies or to buy food). · Romania – On 4 April, the National Company for Road Infrastructure Administration (CNAIR) lifted driving restrictions on vehicles heavier than 7.5 tonnes on the Ploiesti-Brasov section of DN1 (E60) national road. The measure applies until 16 April. Driving restrictions on the Bucharest-Ploiesti section of DN1 are still in force. · Spain – The following restrictions are suspended for the entire duration of the state of emergency: - Week traffic bans for vehicles over 7.5 tonnes - Weekend and festive bans for ADR vehicles - Week, festive and weekend bans for abnormal transport - All traffic bans for transport vehicles in Catalonia and in the Basque Country. · Slovakia – the Slovak police have lifted driving restrictions for goods vehicles heavier than 3.5 tonnes on 10, 12 and 13 April (please note there are no driving restrictions in place on Saturday). Source: IRU members
07.04.2020 DG MOVE issues guidance on the renewal of certain licences and certificates for professional carriers in the EU. Following DG MOVE Director General’s letter to EU Member States requesting them to communicate to the European Commission (EC) services via a single email address, EU-COVID-TRANSPORT@ec.europa.eu, their national measures relative to the COVID-19-related emergency prolongation of the validity of licences and certificates issued to individuals and professional carriers and workers (Flash info published on 27 March) the EC has now published a dedicated Annex, listing these certificates. For road transport, the following main control documents are listed: · Periodic training of drivers, to obtain their Certificates of Professional Competence (CPC), as provided for in Article 8 of Directive 2003/59/EC; · Driving licences, regarding therenewal or, in some cases, the exchange of driving licences, according to Article 7 of Directive 2006/126/EC; · Dangerous goods, covered by Directive 2008/68/EC, including among other things the renewal of driver training certificates for the transport of dangerous goods and the renewal of the dangerous goods safety advisers certificates; · Inspection of the tachograph, as required by Article 23 of Regulation 165/2014; · Periodic roadworthiness tests for motor vehicles and their trailers,as required by Article 5 of Directive 2014/45/EU; · Renewal of community licences,according to Article 6 of Regulation (EC) No 1072/20097 and Article 4 of Regulation 1073/20098; · Renewal of the authorisation for the provision of regular services by bus and coach,according to Article 9 of Regulation 1073/2009; · Renewal of the driver attestation,issued according to Article 5 of Regulation (EC) No 1072/2009; and · Renewal of the certificate of competence for drivers for the transport of live animals, according to Article 17 of Regulation (EC) No 1/20059. To ensure that national authorities are informed of the exceptional measures taken by other Member States and to practice tolerance, the EC will publish the national information on its coronavirus transport platform at https://ec.europa.eu/transport/coronavirus-response_en. Source: European Commission
06.04.2020 Shipments of waste in the context of the coronavirus (COVID-19) crisis. On 30 March 2020, the European Commission issued some specific guidelines in order to ensure the continuation of national and cross-border waste shipments in the EU. The guidelines indicate that the Green Lanes apply mutatis mutandis to the shipments of waste, and invite Member States to implement this principle. In addition, a call is made to abandon paper document treatment and to move to digital document exchange, especially in cases of communications relating to notifications of shipments. Finally, more flexibility is recommended when there are changes in routing which do not involve a Member State that was not included in the original route. Source: European Commission, DG Environm
06.04.2020 On 16 March 2020, the European Commission (EC) adopted a Communication calling for a temporary restriction on non-essential travel to the EU in view of the coronavirus (COVID-19). In order to assist the member states in implementing these new rules, the EC adopted a guidance document last week, providing information on the temporary restriction applying to all non-essential travel to the EU and the effects on visa policy. The main elements of the guidelines are as follows: - The introduction of temporary travel restrictions applying to all non-essential travel from third countries to the EU+ area*; - Minimum service in consulates for processing visa applications; Dealing with overstay caused by travel restrictions, including persons from visa waived third countries. The guidance document clearly states that the temporary restriction should not apply to persons with an essential function or need, including transport personnel. Moreover, member states’ consulates (and possibly external service providers) should remain open and accept/deal with visa applications from those travellers who are exempt, including transport personnel. Additionally, the guidance document says that member states should take into account the measures proposed by the EC on the implementation of Green Lanes when deciding on border crossing points. For a summary of the guidelines per element, please see the document drafted by the IRU secretariat. Source: European Commission, DG HOME *The EU+ area is defined by the European Commission as all Schengen member states (including Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus and Romania) as well as the four Schengen associated states (Iceland, Norway, Switzerland and Lichtenstein).
06.04.2020 SURE - a new temporary instrument worth up to €100 billion to help protect jobs and people in work The European Commission has put forward a new instrument for temporary Support to mitigate Unemployment Risks in an Emergency (SURE). SURE will provide financial assistance, in the form of loans granted on favourable terms from the EU to member states, of up to €100 billion in total. Its goal would be to complement the efforts made by national authorities to support workers affected by the coronavirus (COVID-19) and the containment measures adopted across the EU. The European Commission's proposal for the SURE instrument will need to be approved by the Council. Its duration and scope are limited to tackling the consequences of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic. Source: European Commission
03.04.2020 European Commission issues guidelines on the exercise of the free movement of workers during the coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak Further to its communications on border management and Green Lanes, the European Commission has now issued another communication (see text in all EU official languages), clarifying the conditions for the movement of workers (including transport workers) within the European Union during the coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak. These specific guidelines, which cover a wider sector of workers, further clarify and complement the provisions for international transport workers presented in the Green Lanes Communication, and are without prejudice as far as transport workers are concerned. Member states are also invited to treat self-employed persons in one of the critical occupations listed in these guidelines in the same manner. The listed occupations are as follows: - Health professionals including paramedical professionals; - Personal care workers in health services, including care workers for children, persons with disabilities and the elderly; - Scientists in health-related industries; - Workers in the pharmaceutical and medical devices industry; - Workers involved in the supply of goods, in particular for the supply chain of medicines, medical supplies, medical devices and personal protective equipment, including their installation and maintenance; - Information and communication technology professionals; - Information and communication technicians, as well as other technicians for the essential maintenance of equipment; - Engineering professionals such as energy technicians, engineers and electrical engineering technicians; - Persons working on critical or otherwise essential infrastructures; - Science and engineering associate professionals (including water plant technicians); - Protective services workers; - Firefighters, police officers, prison guards, security guards and civil protection personnel; - Food manufacturing and processing, and related trades and maintenance workers; - Food (and related products) machine operators (includes food production operators); - Transport workers (as defined in the green lanes communication and the letter of the DG MOVE Director General – note IRU), in particular: a) Car, van and motorcycle drivers,heavy truck and bus drivers(includes bus and tram drivers) and ambulance drivers (including those drivers who transport assistance, offered under the Union Civil Protection mechanism as well as those transporting repatriated EU citizens from another member state to their place or origin); b) Airline pilots; c) Train drivers, wagon inspectors, maintenance workshop staff as well as the infrastructure managers’ staff, involved in traffic management and capacity allocation; d) Maritime and inland navigation workers; - Fishermen; - Staff of public institutions, including international organisations in critical functions. The Commission urges member states to establish specific burden-free, fast procedures for border crossings with a regular flow of frontier and posted workers in order to ensure them a smooth passage. This could be done, for instance and where appropriate, by means of dedicated lanes at the border for such workers, or those with specific stickers recognised by neighbouring member states. Health screening for frontier and posted workers must be carried out under the same conditions as nationals exercising the same occupations. Health screening can be carried out before or after the border, depending on the available infrastructure, to ensure traffic remains fluid. Member states should coordinate between themselves to carry out health screening on one side of the border only, in order to avoid overlaps and waiting times. Checks and health screening should not require the workers to leave the vehicles, and should in principle be based on electronic body temperature measurement. Temperature checks on workers should not be carried out more than three times in the same day. For the transport workers referred to in paragraph 19 of the Communication on the implementation of Green Lanes, the specific health screening measures referred to in those guidelines apply. The Commission urges member states to establish specific procedures to ensure the smooth passage for such workers, as well as use the technical committee on the free movement of workers to identify best practices, that can be extended to all member states in order to allow these workers to exercise their occupations without hindrance. Source: European Commission
30.03.2020 Movement of transport workers in the European Union – clarification on documents needed, to certify international transport activity In its letter to the EU Member States of 26 March, the DG MOVE Director General clarified the meaning of “transport workers”, which, for the road transport sector, also covers professional drivers carrying out their tasks internationally. In its Green Lanes Communication (see text in all EU languages) of 23 March, the EC set up the principle of the free movement of transport workers and requested Member States not to subject them to quarantine measures unless they are showing COVID-19 symptoms, as well not to request them to provide a doctor’s certificate or declaration. In their joint statement of 26 March, the EU Heads of States and Governments supported the EC Green Lanes Communication (see item 3), thus making it a joint commitment of all EU Member States. In Annex 3 of the Green Lanes Communication, the Commission introduced an EU template for a certificate for international transport workers, to be signed by the employer, which certifies that the driver is carrying out professional activities in international transport. This template certificate is recommended for use by truck drivers travelling by other means of transport (such as bus or car, and not their truck), to certify their professional activity; this includes drivers driving LCVs who do not have a C or D licence. Professional drivers carrying out their international transport activities with their truck, do not need to have this certificate. In summary, the driver’s ID document, its Certificate for Professional Competence (CPC), and the above certificate for international transport workers, as per Annexe 3 of the EC Green Lanes Communication, established and signed by the employer, should be accepted as sufficient proof of professional activities by the control authorities of EU Member States. No additional documents should be requested from professional drivers. Source: IRU’s own analysis
30.03.2020 Green lanes communication supported by EU Heads of States and available in all EU languages The recent key European Commission communication on green lanes is now available in all EU official languages here. Please note that in their latest statement (26 March), the EU Heads of States and Governments also expressed their support for green lanes with the following statement: “Where temporary internal border controls have been introduced, we will ensure smooth border management for persons and goods and preserve the functioning of the single market, based on the Commission guidelines of 16 March 2020, in accordance with the Schengen Borders Code, and the Commission's guidance on the implementation of "green lanes". This confirms that the implementation of green lanes is a joint commitment of all EU Member States. Source: IRU
28.03.2020 According to information exchanged among IRU members, the large majority of EU Member States allow double-manning, whereby the multi-manning crew is composed of two drivers (Article 4, paragraph o)) of Regulation 561/2006. Specific rules are applied in France, Italy, Spain, and Portugal where a social distance of 1 meter must be respected. In the case of UK, double-manning is not prohibited provided the following conditions are fulfilled: - Minimise contact with the colleagues and customers. Minimum contact is a combination of time and distance. - When close contact is not required then you should be separated by at least two meters. - Regular hand hygiene either using formal hand washing (best) or alcohol gel (good) is important. - Do not bring hands to face / head (for instance to blow your nose) unless you have just washed / gelled hands. - Dispose of any tissue used to blow nose and then wash/gel hands prior to any further action. - If using gloves, change them if physical damage or visible contamination present or if physical damage, or as needed for operator comfort. - If you use PPE, ensure that it (e.g. gloves and / or aprons) is removed safely when you have finished – this is the most important step – and safely disposed of. The information on the UK is based on advice valid at the time of writing, but subject to change. In Finland, double-manning is allowed, provided that the recommended 1-1.5m “social distancing” rule is respected. However, the Uusimaa region has had special restrictive measures recently introduced and double-manning may be an issue when crossing the Uusimaa regional border. Authorities may not consider the second driver as a necessity, as restrictions on the movement of people crossing the regional border is being strictly enforced. For the moment, we do not recommend to make use of double-manning in Hungary. We shall keep monitoring the situation and inform members of any changes. Source: IRU and exchange with IRU members
27.03.2020 On 26 March, DG MOVE Director General, Henrik Hololei, sent a letter to EU Member States requesting them to communicate to the European Commission (EC) services (through a single email address EU-COVID-TRANSPORT@ec.europa.eu) their national measures regarding the COVID-19-related emergency prolongation of the validity of licences and certificates issued to individuals and professional carriers and workers. He also invited national authorities to take this information into account when enforcing the relevant regulatory provisions, in particular regarding professional carriers and workers performing international activities. The information provided by Member States to the EC, should contain, as a minimum, the following: - The relevant EU (or national) legislation and specific provision(s) - A short description of the measure - The envisaged duration of the extension (date, from-to) To ensure that national authorities are informed of exceptional measures taken by other Member States, the EC will publish the national information on its Coronavirus transport platform. Please note that this is a first general statement, to be followed by “specific legal requirements (EU or national) liable to be affected by this situation will be identified and communicated as soon as possible”. DG MOVE services are currently working on this list, including for road transport, and intends to publish it as soon as possible. A dedicated IRU Flash Info will immediately follow. Source: European Commission
22.03.2020 IRU clarifications regarding the exemptions granted by the various EU Member States to driving and rest time rules – Regulation (EC) No 561/2006 A number of EU Member States have granted temporary derogations from driving and rest time rules, pursuant to the provisions of Article 14(2) of Regulation (EC) No 561/2006. The latest official information from the European Commission can be found at its dedicated website at https://ec.europa.eu/transport/modes/road/social_provisions/driving_time_en, under “COVID-19 - Temporary relaxation of drivers' hours rules”. Following several discussions among experts and with the services of the European Commission, the following clarifications can be made: · When these exemptions are granted by EU Member States to international transport (in most cases, but not in all), they apply to all drivers of EU-registered companies on the territory of the given EU Member State; · Enforcement authorities of the various EU Member States have been and will continue to be informed of the various temporary exemptions introduced by the EU Member States, so that they take them into consideration when controlling drivers at the road side; · The European Commission services have formally sent the list of exemptions to the UNECE Secretariat, with the objective to inform also the competent authorities of the AETR Contracting Parties, which are not EU Members, about these exemptions, so that they could possibly be taken into consideration, when EU drivers are subsequently controlled on the territories of AETR Contracting Parties, which are not EU Members; · As a rule, these EU Member States’ exemptions given under the EU Regulation (EC) No 561/2006, are not applicable to drivers from companies registered in AETR Contracting Parties, which are not EU Members. One EU Member State (Poland) has formally and explicitly stated that the exemptions granted on the Polish territory do not apply to drivers from AETR Contracting Parties, which are not EU Members. We therefore strongly recommend to drivers from AETR Contracting Parties, which are not Members of the EU, to respect the AETR Agreement rules. · In exceptional circumstances of the kind drivers are currently meeting on the road and at borders, and according to the provisions of Article 9 of the AETR Agreement, drivers from AETR Contracting Parties, which are not EU Members, “… may depart from the provisions of this Agreement to the extent necessary to ensure the safety of persons, of the vehicle or of its load. The driver shall indicate the nature of and reason for his departure from those provisions on the record sheet of the control device or in his duty roster.” · The IRU is in almost permanent contact with the services of the European Commission and the representative organisations of enforcers in Europe, to discuss, give and obtain advice on these issues.
20.03.2020 The European Commission services have made available a dedicated COVID-19 Temporary relaxation of drivers' hours rules section on its webpage, offering summary information on the various exemptions introduced by EU Member States on driving and rest time rules. It is expected that this will be regularly updated. The table is available here (under “COVID-19 – Temporary relaxation of drivers’ hours rules). Source: European Commission |