Source : European Union / Re-open EU
10.06.2021
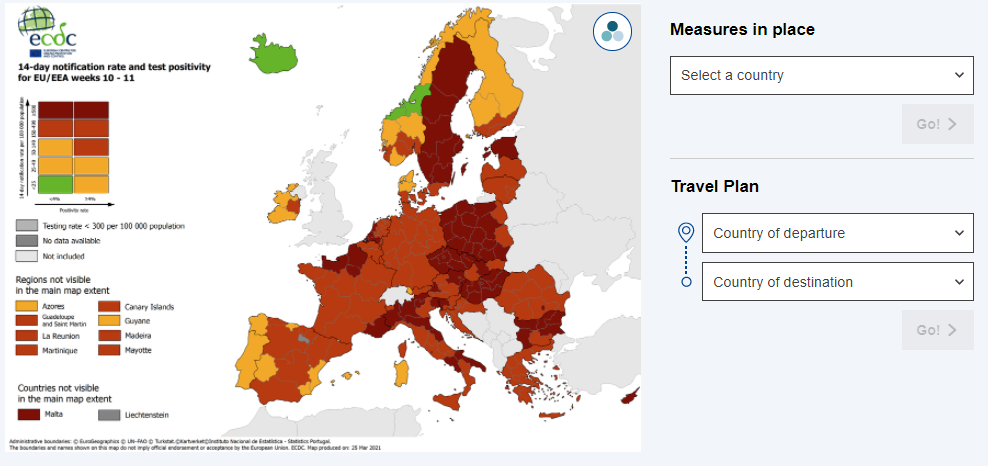
Re-open EU provides information on the various measures in place, including on quarantine and testing requirements for travellers, the EU Digital COVID certificate to help you exercise your right to free movement, and mobile coronavirus contact tracing and warning apps. The information is updated frequently and available in 24 languages. This should help you plan your travel in Europe, while staying safe and healthy.
Information for travellers from third countries to the EU
From 3 June, the revised list of third countries for which travel restrictions should be lifted consists of the following:
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Rwanda
- Singapore
- South Korea
- Thailand
- China, subject to confirmation of reciprocity
- Israel
- Japan
Travel restrictions should also be lifted for the special administrative regions of China Hong Kong and Macao, subject to confirmation of reciprocity.
Residents of Andorra, Monaco, San Marino and the Vatican should be considered as EU residents for the purpose of this recommendation.
EU Digital COVID Certificates
The EU Digital COVID Certificate (available from 1 July 2021) provides proof that a person has either:
- been vaccinated against COVID-19 (vaccine type and manufacturer, number of doses, date of vaccination);
- received a negative test result, PCR or rapid antigen, with the name of the test, date and time of test, test centre and result (self-tests are not valid);
- recovered from COVID-19.
When travelling, holders of the EU Digital COVID Certificate will have the same rights as citizens of the visited Member State who have been vaccinated, tested or recovered.
The certificate provides a standardised recognition of the holder's status related to vaccination, recovery from COVID or test result. Each country continues to be responsible for the definition of its own entry requirements and rules, which are not standardised at the EU level. This means that what you will be eligible for, upon presentation of this certificate, depends on the measures and entry rules in place at your country of destination.
How does it work:
- Member States issue a certificate automatically or upon request, which is issued either digitally or on paper, and has a QR code with an electronic signature;
- Citizens store the certificate in their digital app or wallet and can use it when they travel;
- When the verifier asks the citizen for the certificate, the QR code is shown and the digital signature is verified.
Find out more:
Information on the EU Digital COVID Certificate
Press Release
Questions & Answers
Factsheet
01.04.2021
Travel Plan tool
Source: https://reopen.europa.eu/en/from-to/*/
18.12.2020
EU-UK relations: parliament adopts temporary contingency measures
On Friday, Parliament adopted measures to ensure basic road and air connections in case no agreement is reached on EU-UK future relations.
- Basic air connectivity: the temporary rules ensuring certain air services between the UK and the EU continue for a maximum of six months were adopted with 680 votes in favour (3 against, 4 abstentions). This includes rights for UK and EU air carriers to continue to fly over and make technical stops on EU territory, as well as serve direct routes to the EU. Also a limited number of specific pandemic-related cargo flights will be allowed.
- Aviation safety: the regulation ensuring various certificates for products, parts, appliances and companies remain valid was adopted with 680 votes in favour (3 against, 4 abstentions). This will avoid UK and EU aircraft that use these products and services being grounded.
- Basic road connectivity: the temporary rules ensuring road freight and road passenger transport for a maximum of six months were adopted with 680 votes in favour (4 against, 3 abstentions). This will allow carriage of goods as well as coach and bus services coming to Europe and going to the UK to continue.
Background
EU rules will no longer apply to and in the UK after the end of the transition period. The targeted contingency measures aim to avoid serious traffic disruptions and considerable delays in case there is no agreement on EU-UK future relations in place by 1 January 2021. The contingency measures will cease to apply, if an agreement is reached.
MEPs also approved the Commission’s proposal to extend reciprocal access by EU and UK vessels to each other’s waters until 31 December 2021 by 677 votes in favour, 4 against and 6 abstentions. Read more here.
Next steps
All temporary rules have to be adopted by the Council. They will enter into force after publication in the EU Official Journal and become applicable if a similar set of measures is adopted by the UK.
12.11.2020
EU countries have agreed on a coordinated approach to the restriction of free movement in response to the coronavirus pandemic. This includes a colour code for the classifications of regions - green, orange, yellow and grey - based on the epidemiological situation there. They also agreed on common criteria that they should apply when deciding whether to introduce travel restrictions, a common approach for travelers from ‘red areas’ (testing and self-quarantine), as well as on providing more clear and timely information to the public.
This website will gradually provide more information as it becomes available.
Information for travellers from third countries to the EU
The Council updated the list of countries for which travel restrictions should be lifted. This list will continue to be reviewed and, as the case may be, updated every two weeks.
Based on the criteria and conditions set out in the recommendation, member states should gradually lift the travel restrictions at the external borders for residents of the following third countries:
- Australia
- Japan
- New Zealand
- Rwanda
- Singapore
- South Korea
- Thailand
- Uruguay
- China, subject to confirmation of reciprocity
Travel restrictions should also be gradually lifted for the special administrative regions of China Hong Kong and Macao, subject to confirmation of reciprocity.
Residents of Andorra, Monaco, San Marino and the Vatican should be considered as EU residents for the purpose of this recommendation.
Source : https://reopen.europa.eu/en
Source: European Commission
13.10.2020
A common approach to travel measures
On 13 October, EU Member States adopted a Council Recommendation on a coordinated approach to the restriction of free movement in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. This Recommendation is based on the Commission’s proposal adopted on 4 September.
A common approach to travel measures in the EU
The Recommendation sets out four key areas where Member States will coordinate their efforts:
- a common mapping system based on a colour code (green, orange, red, grey)
- common criteria for Member States when deciding whether to introduce travel restrictions
- more clarity on the measures applied to travellers from higher-risk areas (testing and self-quarantine)
- providing clear and timely information to the public.
Factsheet - COVID-19 - A coordinated approach to the restriction of free movement
13 October 2020
English DownloadPDF
30.06.2020
Temporary Restriction on Non-Essential Travel to the EU
The Council adopted on 30 June, a Recommendation on the gradual lifting of the temporary restrictions on non-essential travel into the EU. Travel restrictions should be lifted for countries listed in the recommendation (consult the website). Upon revision by Member States and the Council, this list will be reviewed every two weeks.
Start date: 01.07.2020
Further information: https://ec.europa.eu/info/live-work-travel-eu/health/coronav...
More info: https://ec.europa.eu/info/live-work-travel-eu/health/coronavirus-respo...
Source: https://ec.europa.eu/transport/coronavirus-response_en
Travel restrictions
On 17 March 2020, EU Member States agreed on coordinated action at the external borders based on the recommendation by the Commission to restrict non-essential travel for an initial period of 30 days. This was prolonged several times until 30 June 2020.On 11 June 2020, the Commission adopted a Communication which set out an approach to progressively lift the restriction afterwards.
On 25 June, the Commission adopted a draft proposal for a Council Recommendation indicating that travel restriction should be lifted for countries selected together by Member States, on the basis of a set of principles and objective criteria including the health situation, the ability to apply containment measures during travel, and reciprocity considerations, taking into account data from relevant sources such as ECDC and WHO. Based on this approach, the Council adopted on 30 June, a Recommendation on the gradual lifting of the temporary restrictions on non-essential travel into the EU. Travel restrictions should be lifted for countries listed in the recommendation. Upon revision by Member States and the Council, this list will be reviewed every two weeks.
Based on the criteria and conditions set out in the Recommendation, as from 1 July Member States should start lifting the travel restrictions at the external borders for residents of the following third countries:
- Algeria
- Australia
- Canada
- Georgia
- Japan
- Montenegro
- Morocco
- New Zealand
- Rwanda
- Serbia
- South Korea
- Thailand
- Tunisia
- Uruguay
- China, subject to confirmation of reciprocity
Residents of Andorra, Monaco, San Marino and the Vatican should be considered as EU residents for the purpose of this recommendation.
While the restrictions on non-essential travel and their lifting depend on the traveller’s place of residence, the visa requirement continues to depend on nationality. If a traveller resides in a country where restrictions have been lifted, but is a national of a visa-required country, he or she must apply at the consulate of the Member State to which he wishes to travel to, in his or her country of residence.
For all other third countries not on this list, Member States and Schengen Associated countries are temporarily suspending all non-essential travel from those third countries to the EU+ area, meaning that only certain categories of travellers could be authorised entry. The “EU+ area” includes 30 countries: 26 out of the 27 EU Member States as well as the four Schengen Associated States: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. Ireland does not currently apply the travel restriction.
Travel restrictions aim to reduce the number of travellers entering the European Union. The aim is to restrict the spread of the coronavirus and protect public health within the EU, as well as to prevent the virus from spreading from the EU to other countries.
As the epidemiological situation in and outside the EU evolves and travel restrictions at the EU’s external borders gradually start to be lifted, visa operations will also resume gradually. On 11 June 2020, the Commission published a Guidance for a phased and coordinated resumption of visa operations.
The rules for applying for a short-stay visa remain unchanged. Member States’ consulates and external service providers will, however, have adapted practical aspects of access management, hygiene measures, payment methods etc. Applicants are advised to verify websites for information of the procedure to follow in advance.
Information on travel restrictions in place should be available on the websites of the relevant national authorities (e.g. Ministries of Interior and Foreign Affairs). A daily summary of flight and passenger restrictions is available on the Eurocontrol website and is entitled ‘Covid Notam (notice to airmen) summary’.
Exemptions from travel restrictions
The following categories of persons are exempt from the temporary travel restriction to the EU+ area from the third countries which are not on the list agreed by the Member States:
(a) Union citizens within the meaning of Article 20(1) TFEU and third-country nationals who, under agreements between the Union and its Member States, on the one hand, and those third countries, on the other hand, enjoy rights of free movement equivalent to those of Union citizens, as well as their respective family members.
(b) third-country nationals who are long-term residents under the Long-term Residence Directive or deriving their right to reside from other EU Directives or national law or who hold national long-term visas, as well as their respective family members.
The temporary travel restrictions should also not apply to people with an essential function or need, including
- healthcare professionals, health researchers, and elderly care professionals
- frontier workers
- seasonal workers in agriculture
- transport personnel
- Diplomats, staff of international organisations and people invited by international organisations whose physical presence is required for the well-functioning of these organisations, military personnel and humanitarian aid workers and civil protection personnel in the exercise of their functions;
- passengers in transit
- passengers travelling for imperative family reasons
- seafarers
- persons in need of international protection or for other humanitarian reasons;
- third-country nationals travelling for the purpose of study;
- highly qualified third-country workers if their employment is necessary from an economic perspective and the work cannot be postponed or performed abroad.
Exemption details
Seasonal workers
Temporary travel restrictions should not apply to travel by people with an essential function or need, including seasonal workers in agriculture.
Medical professionals
Temporary travel restrictions should not apply to travelling by people with an essential function or need, including healthcare professionals, health researchers, and elderly care professionals.
EU citizens’ family members*
The temporary travel restriction must exempt nationals of all EU Member States and Schengen Associated States, as well as their family members.
*Family members (as defined in Articles 2(2) and 3(2) of Directive 2004/38/EC):
Articles 2(2):
(a) the spouse;
(b) the partner with whom the Union citizen has contracted a registered partnership, on the basis of the legislation of a Member State, if the legislation of the host Member State treats registered partnerships as equivalent to marriage and in accordance with the conditions laid down in the relevant legislation of the host Member State;
(c) the direct descendants who are under the age of 21 or are dependants and those of the spouse or partner as defined in point (b);
(d) the dependent direct relatives in the ascending line and those of the spouse or partner as defined in point (b);
Articles 3(2):
(a) any other family members, irrespective of their nationality, not falling under the definition in point 2 of Article 2 who, in the country from which they have come, are dependants or members of the household of the Union citizen having the primary right of residence, or where serious health grounds strictly require the personal care of the family member by the Union citizen;
(b) the partner with whom the Union citizen has a durable relationship, duly attested.
Transport personnel
The temporary travel restrictions should not apply to transport personnel. This category should be interpreted broadly.
Someone claiming asylum
The temporary travel restrictions should not apply to travel by people with an essential need, including persons in need of international protection or for other humanitarian reasons.
Third-country students
This new exception covers third-country students starting or continuing their studies in the EU in the academic year 2020/21. A student is defined in Article 3(3) of the EUs Students and Researchers Directive 2016/801 as “a third-country national who has been accepted by a higher education institution and is admitted to the territory of a Member State to pursue as a main activity a full-time course of study leading to a higher education qualification recognised by that Member State, including diplomas, certificates or doctoral degrees in a higher education institution, which may cover a preparatory course prior to such education, in accordance with national law, or compulsory training.”
Third-country workers
This new exception covers third-country workers who, because of their high level of skills and knowledge, are needed to contribute to the EU’s post-COVID economic recovery. It may include those whose application for permits under the EUs Blue Card Directive 2009/50, the EU ICT Directive 2014/66, the Directive 2016/801 as Researchers, or under a national scheme for skilled migrants was approved, but who were until now prevented from entering the EU due to the entry ban.
Further information
Schengen visa holders currently in the EU
Visa holders present in the Schengen area who cannot leave at the expiry of their short-stay visa must contact the authorities of the Member State in which they are located to ask for an extension of their visa. A visa may generally be extended to allow for a total stay of 90 days in a 180 days period.
List of relevant national authorities in Member States
Nationals of visa-waived third countries who have remained in the Schengen area beyond the permitted 90-day stay
For nationals of visa-waived third-countries who are compelled to stay beyond the extended 90/180 days, the competent national authorities should extend the validity of the authorisations for legal stay, issue a new one or take other appropriate measures ensuring a continued right to stay on their territory. Information is available on the websites of Member States’ national authorities.
Irish citizens (and residents)
Although Ireland is not part of the Schengen area, all EU citizens and their family members must be exempt from the temporary travel restriction.
United Kingdom citizens
UK nationals are still to be treated in the same way as EU citizens until the end of the Brexit transition period (31.12.2020). Therefore, during that time UK nationals and their family members are exempt from the temporary travel restriction.
Transit through other EU Member States (road transit or transfer at airport)
EU citizens who are returning to their Member State of nationality or residence, as well as their family members, irrespective of their nationality, should be allowed onward transit. Given the reduced availability of commercial flights, ‘onward transit’ should cover any means of transportation.
EU citizens returning to their Member State of nationality or residence from a third country
The temporary restrictions on non-essential travel to the EU do not apply to returning EU citizens and citizens of the Schengen Associated States.
Expired travel documents due to an unexpectedly extended stay abroad
EU citizens and their family members who are not in possession of a valid passport and/or visa should be allowed to enter the EU territory, if they can prove by other means that they are EU citizens or family members of an EU citizen. Possession of an expired passport should be deemed to constitute proof by other means in the current situation. Family members should always be able to prove that they are indeed family members of the EU citizen.
Transit through airports located in an EU Member State or Schengen Associated States
Passengers travelling from a non-EU country to another non-EU country may transit through the international transit area of airports located in the Schengen area. Rules regarding airport transit visa requirements continue to apply.
Temporary Restriction on Non-Essential Travel to the EU (17.03.2020)
EU Leaders agreed to temporary restriction of non-essential travel from third countries into the EU area for 30 days. Any possible prolongation of this period should be assessed depending on further developments. The temporary travel restriction foresees exemptions for nationals of all EU Member States and Schengen Associated States (Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland; whilst UK nationals are still to be treated in the same way as EU citizens until end 2020), for the purposes of returning to their homes. Exceptions are also foreseen for travellers with an essential function or need.
Start date: 17.03.2020
End date: 30 days from starting date
Further information: https://eeas.europa.eu/headquarters/headquarters-homepage_en