Source: Federal Office of Public Health FOPH
02.05.2022
COVID-19 travel restrictions have been lifted in Switzerland. Travellers do not need to provide proof of vaccination, recovery from COVID-19 or a negative test result. In addition, all domestic pandemic measures have been lifted.
Health measures will still apply for travellers arriving from countries or areas of variant concern. All travellers are reminded to consult lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health. Currently, there is no country or area on the list.
__________________________________________________________________________________
01.04.2022
What are the rules to enter this country from an EU Member State or Schengen Associated country?
Switzerland has lifted COVID-19 border health measures. It is no longer necessary for travellers from EU member states and Schengen Associated countries to submit contact data or provide proof of vaccination, recovery or a negative test. Health measures remain in place for travellers arriving from a country or area of variant concern.
Travellers are reminded to consult lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration to check their national status for entry.
Entry from a country or area of variant concern
- These travellers must complete the Entry Form before entering Switzerland.
- They must present a negative PCR (maximum 72 hours) or antigen (maximum 48 hours) test.
- Travellers have to undergo mandatory quarantine. Fully vaccinated or recovered travellers are exempted from the quarantine requirement, if they enter from a country or area with a variant of concern that is not immune evasive. Currently, there are no countries on the list.
- Vaccines authorised by Swissmedic,the European Medicines Agency and the WHO are valid for 270 days. For the Janssen vaccine it is 270 days from the 22nd day of administration.
- Proof of recovery can be provided in the form of a positive result from a PCR or antigen test. The validity of proof of recovery starts from the 11th day after the positive test result and lasts 180 days.
What are the rules to enter this country from outside an EU Member State or Schengen Associated country?
Switzerland has lifted its vaccination, recovery or a negative test border health measures. It is no longer necessary for travellers to submit contact data or provide proof of vaccination, recovery or a negative test. Please note, however, that third country nationals who wish to enter Switzerland from a high-risk country for a short stay of up to 90 days need to be fully vaccinated and have to fulfill the normal entry requirements when crossing the border (e.g. valid visa and travel documents).
Additionally, health measures remain in place for travellers arriving from a country or area of variant concern. Travellers are reminded to consult lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration.
Travellers can check their travel status and whether they are approved for entry at the Travelcheck site.
All travellers from non-EU and Schengen Associated countries can check their status according to two lists:
1. Entry from a non high-risk or high-risk country:
- Entry from a non high-risk country is possible provided that the normal entry requirements are met when crossing the border (e.g. valid visa and travel documentation).
- Entry from a high-risk country requires proof of vaccination.
- Vaccines authorised by Swissmedic, the European Medicines Agency and the WHO are valid for 270 days from the date of administration in full.
- Proof of recovery can be provided in the form of a positive result from a PCR or antigen test. The validity of proof of recovery starts from the 11th day after the positive test result and lasts for 180 days.
- These restrictions do not apply to children and adolescents under the age of 18.
2. Entry from a country or area of variant concern
- Travellers can determine whether or not they are entering from a country or area classified as one of variant concern.
- These travellers must complete the online Entry Form before entering Switzerland.
- They must present a negative PCR (maximum 72 hours) or antigen (maximum 48 hours) Travellers have to underg from a country or area with a variant of concern that is not immune evasive. Currently, there are no countries on the list.
- Vaccines authorised by Swissmedic, the European Medicines Agency and the WHO are valid for 270 days from the date of administration in full. For the Janssen vaccine it is 270 days from the 22nd day of administration.
- Proof of recovery can be provided in the form of a positive result from a PCR or antigen test. The validity of proof of recovery starts from the 11th day after the positive test result
Children under age 18 are exempt from the entry rules.
Learn more:
Federal Office of Public Health
State Secretariat for Migration
May I transit this country?
It is no longer necessary for travellers from EU and Schengen Associated countries to provide contact data, proof of vaccination, recovery or a negative test. The sole exception is for travellers entering Switzerland from a country or area of variant concern or from high-risk countries. Travelcheck allows travellers to assess their status for entry and transit.
Transit from a third country considered high-risk to a Schengen state
Transit from a third country to a Schengen state is considered an entry into Switzerland. Please refer to the above information on entry into Switzerland.
If you have not been vaccinated or recovered from COVID-19, but your destination country in the Schengen Area has approved your entry for up to 90 days, you may only enter the Schengen area by travelling directly to your destination country i.e. you may not travel through Switzerland.
Transit from a third country considered high-risk to another third country
It is not possible to enter Switzerland from a third country that is considered high-risk in order to travel to another country outside the Schengen area, unless transiting through Zurich or Geneva airports. In such cases, travellers do not actually enter Switzerland but remain in the transit area of the airport.
Transit from a third country considered not high-risk to another third country
It is only possible to enter Switzerland from a third country that is considered high-risk in order to travel on to another country outside the Schengen area, when transiting through Zurich and Geneva airports. In such cases, travellers do not actually enter Switzerland but remain in the transit area of the airport.
General measures
From 17 February, there is no longer a requirement to present a COVID-19 certificate to enter public facilities and venues such as shops, cinemas, theatres and restaurants, or to attend events. The recommendation to work from home is lifted.
The Swiss authorities will continue to issue COVID-19 certificates recognised by the EU. It must be assumed that other countries will continue to require a COVID certificate for travel and in other settings. The cantons will, as they requested, still be able to impose a certificate requirement.
Be aware that specific cantonal rules may apply.
Restrictions at the regional or local level
Consult the corresponding canton to find out which cantonal measures apply. Where the cantonal measures are stricter than the national measures, then these must be observed. The links to information provided by the cantons can be found on the website www.ch.ch (in German, French or Italian).
Use of facemasks
There is no national requirement to wear masks. However, the cantons have the possibility to impose a mask-requirement at the cantonal level (e.g. medical institutions).
Quarantine
There are currently no countries of variant on the mandatory quarantine list. However, travellers from outside the EU/Schengen area are reminded to consult lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration to check their national status for entry.
Learn more:
Federal Office of Public Health
National website with coronavirus-related information for TOURISM
Useful Info for tourists
See: www.myswitzerland.com;
www.bag.admin.ch
_______________________________________________________________________
10.03.2022
Coronavirus: Entering Switzerland
Entry to Switzerland is still subject to the entry requirements stipulated by the State Secretariat for Migration (SEM). In addition, people entering Switzerland from a state or area with a variant of concern must observe the health-related measures at the border. The interactive travel check tool will provide you with information on your individual situation when entering Switzerland.
- Notice for foreign nationals
- Entry form
- Test
- Travel quarantine
- Contact details of the cantonal authorities
- Distancing and hygiene recommendations in Switzerland
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Notice for foreign nationals
You may not be allowed to enter Switzerland. Before you travel, you should check the following:
- Am I even allowed to travel to Switzerland? The interactive travel check and the website of the State Secretariat for Migration (SEM) will give you more information on this.
- If entry is permitted: People entering Switzerland from a country with a variant of concern must observe the health-related measures at the border. You will find information on the individual measures on this site.
For everyone entering Switzerland, the list of countries with a virus of concern determines whether they must observe further health-related measures at the border on arrival. Are you entering Switzerland from a country or area with a variant of concern? Then you may have to complete an entry form, get tested and/or go into travel quarantine. You will find information on the individual measures on this site.
Currently no countries or areas with a variant of concern are listed. This means that there is no test or quarantine requirement at present for entering Switzerland, and also that people entering do not have to fill out an entry (passenger locator) form. Continue to observe the entry restrictions set down by the State Secretariat for Migration (SEM).
Entry form
Currently you do not have to fill out an entry form for entry to Switzerland.
It is the list of countries with a variant of concern that determines whether you have to complete an entry form. Since there are currently no countries or areas on this list, until further notice people arriving can enter Switzerland without an entry form.
Test
Currently you do not have to present a negative test result to enter Switzerland.
Note that the airline or long-distance bus company can nevertheless demand a test on boarding. For this reason you should find out directly from the airline or long-distance bus company what rules they apply.
Travel quarantine
Since no countries or areas with a variant of concern are listed, there is currently no quarantine requirement for people entering Switzerland.
Contact details of the cantonal authorities
If after entering Switzerland you must go into travel quarantine, notify the canton responsible accordingly within two days of entry.
| Canton | Contact details |
|---|---|
| Aargau | Homepage (In German) |
| Appenzell Ausserrhoden | Online application form (In German) |
| Appenzell Innerrhoden | Homepage (In German) |
| Basel-Landschaft | Homepage (In German) |
| Basel-Stadt | Homepage |
| Bern | Online application form |
| Fribourg | Homepage (In German) |
| Geneva | Online application form |
| Glarus | Online application form (in German) |
| Graubünden | |
| Jura | |
| Lucerne | Homepage (In German) |
| Neuchâtel | Homepage (In French) |
| Nidwalden | Homepage (In German) |
| Obwalden | |
| St. Gallen | Online application form (In German) |
| Schaffhausen | Homepage (In German) |
| Schwyz | Online application form (In German) |
| Solothurn | Homepage (In German) |
| Thurgau | Online Application Form (In German) |
| Ticino | Online application form (In Italian and in English) |
| Uri | Homepage (In German) |
| Valais | Homepage (In German) |
| Vaud | Homepage (In French) |
| Zug | Online application form (In German) |
| Zurich | Homepage (In German) |
| Principality of Liechtenstein | Homepage (in German) |
Distancing and hygiene recommendations in Switzerland
On the Measures and Ordinances page you will see what rules apply on a nationwide basis. In other words, these coronavirus-related measures at the very least apply all over Switzerland; the cantons may have stricter measures. This means you should also find out from the canton to which you are travelling what rules apply there.
Please also observe the distancing and hygiene recommendations that apply in Switzerland. This is the best way to protect yourself and others from infection with the coronavirus.
Have you started to have symptoms of illness after entering Switzerland? Take them seriously and follow the instruction on the Isolation and contact with a person who has tested positive page.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
01.03.2022
What are the rules to enter this country from an EU Member State or Schengen Associated country?
Switzerland has lifted COVID-19 border health measures. It is no longer necessary for travellers from EU member states and Schengen Associated countries to submit contact data or provide proof of vaccination, recovery or a negative test. Health measures remain in place for travellers arriving from a country or area of variant concern.
Travellers are reminded to consult lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration to check their national status for entry.
Entry from a country or area of variant concern
- These travellers must complete the Entry Form at least 48 hours before departure.
- They must present a negative PCR (maximum 72 hours) or antigen (maximum 48 hours) test.
- Travellers have to undergo mandatory quarantine. Fully vaccinated or recovered travellers are exempted from the quarantine requirement, if they enter from a country or area with a variant of concern that is not immune evasive.
- Vaccines authorised by Swissmedic and the European Medicines Agency are valid for 270 days. For the Janssen vaccine it is 270 days from the 22nd day of administration.
Entering this country with the EU Digital COVID certificate
Switzerland has lifted COVID-19 border health measures. It is no longer necessary for travellers from EU and Schengen Associated countries to provide contact data, proof of vaccination, recovery or a negative test. The sole exception is for travellers entering Switzerland from a country or area of variant concern.
Travellers are reminded to consult lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration to check their national status for entry.
Entering this country without the EU Digital COVID certificate or with a certificate not compliant with national requirements
Switzerland has lifted COVID-19 border health measures. It is no longer necessary for travellers from EU and Schengen Associated countries to provide contact data, proof of vaccination, recovery or a negative test. Please note, however, that third country nationals who wish to enter Switzerland from a high-risk country for a short stay of up to 90 days need to be fully vaccinated and have to fulfill the normal entry requirements when crossing the border (e.g. valid visa and travel dociuments).
Additionally, health measures remain in place for travellers arriving from a country or area of variant concern. Travellers are reminded to consult lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration to check their national status for entry.
What are the rules to enter this country from outside an EU Member State or Schengen Associated country?
Switzerland has lifted its vaccination, recovery or a negative test border health measures. It is no longer necessary for travellers to submit contact data or provide proof of vaccination, recovery or a negative test. Please note, however, that third country nationals who wish to enter Switzerland from a high-risk country for a short stay of up to 90 days need to be fully vaccinated and have to fulfill the normal entry requirements when crossing the border (e.g. valid visa and travel documents).
Additionally, health measures remain in place for travellers arriving from a country or area of variant concern. Travellers are reminded to consult lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration.
Travellers can check their travel status and whether they are approved for entry at the Travelcheck site.
All travellers from non-EU and Schengen Associated countries can check their status according to two lists:
1. Entry from a non high-risk or high-risk country:
- Entry from a non high-risk country is possible provided that the normal entry requirements are met when crossing the border (e.g. valid visa and travel document).
- Entry from a high-risk country requires proof of vaccination or, if under 18, travel with an adult. Vaccines authorised by Swissmedic and the European Medicines Agency are valid for 270 days. Holders of vaccines authorised by the WHO emergency list are eligible to apply for a Swiss COVID certificate.
2. Entry from a country or area of variant concern
- Travellers can determine whether or not they are entering from a country or area classified as one of variant concern.
- These travellers must complete the online Entry Form at least 48 hours before departure.
- They must present a negative PCR (maximum 72 hours) or antigen (maximum 48 hours) test.
- Fully vaccinated or recovered travellers might be exempted from the quarantine requirement, if they enter the country or area with a variant of concern that is not immune evasive.
- Vaccines authorised by Swissmedic and the European Medicines Agency are valid for 270 days. For the Janssn vaccine it is 270 days from the 22nd day of administration.
Learn more:
Federal Office of Public Health
State Secretariat for Migration
______________________
You can find the latest information on air travel regulations for this country on the IATA website.
You can also find information about your passenger rights on our portal for citizens.
Documents you need to travel in Europe
Health cover for temporary stays
What are the rules if I go abroad from this country, and when I return from abroad?
Travellers are advised to check with the Federal Department of Foreign Affairs as to whether the country of their destination is classified as high-risk or virus variant. The web site provides information in German, French and Italian. There are no specific COVID-19 entry rule requirements for travellers arriving in Switzerland from EU and Schengen Associated countries.
May I transit this country?
It is no longer necessary for travellers from EU and Schengen Associated countries to provide contact data, proof of vaccination, recovery or a negative test. The sole exception is for travellers entering Switzerland from a country or area of variant concern or from high-risk countries. Travelcheck allows travellers to assess their status for entry and transit.
Transit from a third country considered high-risk to a Schengen state
It is only possible to enter Switzerland from a high-risk country in order to travel on to another Schengen state for a short stay of up to 90 days if you can prove that you have been vaccinated. Persons under 18 may enter Switzerland if they are travelling with an adult who has been vaccinated. Otherwise, normal requirements to enter Switzerland apply.
If you have not been vaccinated, but your destination country in the Schengen Area has approved your entry for up to 90 days, you may only enter the Schengen area by travelling directly to your destination country i.e. you may not travel through Switzerland.
Transit from a third country considered high-risk to another third country
It is not possible to enter Switzerland from a third country that is considered high-risk in order to travel to another country outside the Schengen area, unless transiting through Zurich or Geneva. In such cases, travellers do not actually enter Switzerland but remain in the transit area of the airport.
Transit from a third country considered not high-risk to another third country
Entry from a third country not on the high-risk list for onward travel to another country outside the Schengen area is possible subject to normal entry and transit rules.
General measures
From 17 February, there is no longer a requirement to present a COVID-19 certificate to enter public facilities and venues such as shops, cinemas, theatres and restaurants, or to attend events. The recommendation to work from home is lifted.
The Swiss authorities will continue to issue COVID-19 certificates recognised by the EU. It must be assumed that other countries will continue to require a COVID certificate for travel and in other settings. The cantons will, as they requested, still be able to impose a certificate requirement.
Be aware that specific cantonal rules may apply.
Use of facemasks
Facemasks must be worn when using public transportation and in healthcare facilities.
Indoor and outdoor meetings, public or private gatherings and events
There are no restrictions on attendance.
Safety measures for public transportation
Passengers over age 12 must wear facemasks or respirators when aboard public transportation.
Places of worship
Churches and places of worship are open and religious events can be held.
Quarantine
There are currently no countries of variant on the mandatory quarantine list. However, travellers from outside the EU/Schengen area are reminded to consult lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration to check their national status for entry.
Learn more:
Federal Office of Public Health
Tourist accommodations
All shops are open.
Catering establishments
All catering establishments are open. There are no restrictions on attendees.
Cinemas, museums and indoor attractions
All cultural, leisure and sports facilities are open.
Personal care services
Personal care services are open.
Ski facilities
There are no restrictions to use ski facilities.
Information on Tourism at National level
National website with coronavirus-related information for TOURISM
Useful Info for tourists
See: www.myswitzerland.com;
www.bag.admin.ch
__________________________________________________________________________________
16.02.2022
Coronavirus: Federal Council to lift measures – mask requirement on public transport and in healthcare institutions and isolation in the event of illness to remain until end of March
Bern, 16.02.2022 - From Thursday, 17 February, masks and COVID certificates will no longer be required to enter shops, restaurants, cultural venues and other public settings and events. The requirement to wear masks in the workplace and the recommendation to work from home will also end. At its meeting on 16 February, the Federal Council took the decision to lift the majority of measures in place to contain the coronavirus pandemic. Only the requirements to isolate in the event of a positive test and to wear masks on public transport and in healthcare institutions will remain in place until the end of March to protect those at high risk, after which the situation status will return to normal.
The epidemiological situation continues to develop positively. Thanks to the high level of immunity among the population, it is unlikely that the healthcare system will be overburdened despite the continued high level of virus circulation. For the Federal Council, this means that the conditions are in place for a rapid normalisation of social and economic life. After consulting the cantons, the social partners, the parliamentary committees and the associations concerned, it is lifting most of the measures in place to combat the pandemic. Since May 2021, it has based its
measures on available capacity in the healthcare system.
Consultation: Majority for swift lifting of measures
On 2 February, the Federal Council submitted two options for lifting measures for consultation. A clear majority of respondents came out in favour of lifting most of the remaining measures with immediate effect. At the same time, they favoured retaining the requirement to wear masks in healthcare institutions and on public transport as long as infection rates remain high.
From 17 February: Almost all measures lifted
From Thursday, 17 February, the following protective measures will be lifted throughout Switzerland:
- mask requirement in shops, restaurants, as well as in other public settings (facilities, venues and events)
- mask requirement in the workplace
- access restrictions regulated by COVID certificate (3G, 2G and 2G+-rule) to facilities and venues such as cinemas, theatres and restaurants, as well as events
- permit requirement for large-scale events
- restrictions on private gatherings
In agreement with the Federal Council, voluntary capacity restrictions in the retail sector and in cablecars and gondolas will be lifted.
Recommendation to work from home lifted - employers still responsible for protecting staff
The recommendation issued by the FOPH to work from home is also lifted. Employers are therefore free to determine whether staff should work from home or wear masks in the workplace. However, under employment law, they are required to take the necessary steps to protect staff.
Rules to protect employees at especially high risk will remain in place until the end of March.
Isolation and mask requirement in certain settings until 31 March
Given that infection rates remain very high and that the virus can still cause severe cases of illness, the Federal Council is maintaining two protective measures in the COVID-19 Special Situation Ordinance until the end of March. Depending on the epidemiological situation, an earlier lifting of the measures is possible.
Persons who have tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 will still be required to isolate. This is to prevent people who are highly infectious from infecting others.
The mask requirement on public transport and in healthcare institutions will remain in place. Residents of old people's and nursing homes are exempt. The cantons are free to impose stricter protective measures or to exempt certain institutions from the mask requirement. Individual establishments may still stipulate that visitors must wear a mask, for example in medical practices or hairdressing salons.
End of special situation on 1 April
The provisions of the COVID-19 Special Situation Ordinance on isolation and the mask requirement on public transport and in healthcare institutions will still apply until the end of March. If the epidemiological situation continues to evolve as expected, the ordinance will expire on 1 April and the situation status will return to normal.
Provisions based on the federal government's powers under the Epidemics Act (e.g. on international travel and on covering the costs of therapeutic products) will also remain in force. Legal provisions on COVID certificates and the coverage of test costs based on the COVID-19 Act will also remain in force.
EU-compatible COVID certificates will still be issued
The lifting of the certificate requirement means that COVID certificates valid only in Switzerland will no longer be issued. These ‘Swiss' COVID certificates were introduced last autumn to allow further groups of people to access facilities, venues and events subject to a certificate requirement.
However, the Swiss authorities will continue to issue COVID certificates recognised by the EU. It must be assumed that other countries will continue to require a COVID certificate for travel and in other settings. The cantons will, as they requested, still be able to impose a certificate requirement.
Changes with regard to testing
The general recommendation for repetitive testing in companies will no longer apply and its funding will end. Repetitive testing will only continue to be funded in certain, narrowly defined areas, such as in healthcare and socio-medical institutions, and in companies involving
in maintaining critical infrastructure that are specified by the cantons. This will help to protect people who are at especially high risk. It will also prevent large numbers of staff from being absent due to illness and isolation.
For schools, the recommendation for repetitive testing and its funding by the federal government will remain until the end of March, as virus circulation among younger age groups remains very high. The cost of individual tests will continue to be covered: antigen tests in all cases, and PCR tests for people with symptoms or after close contact with people who have tested positive.
Loss of earnings payments to continue for certain groups of people
Once measures are lifted, there will no longer be a need for most economic support measures. Therefore, claims for loss of earnings as a result of business closures, event bans, reduced working hours and a shortfall in outside care will no longer be possible from 17 February.
An exception applies until 30 June for persons working in the events sector whose employment is significantly restricted due to measures to combat the COVID-19 epidemic. An exception also applies until the end of March for persons who have to interrupt work due to their need to protect themselves. Overall, the rapid lifting of measures should result in a reduction in expenditure of several hundred million Swiss francs
compared to the budgeted amounts.
Changes to entry rules
Health-related measures for persons entering the country are to be lifted. It will no longer be necessary to provide proof of vaccination, recovery or a negative test or complete an entry form.
Changes regarding coverage of costs for therapeutic products in out-patient treatment
For the time being, the funding of new therapeutic products that can be used to treat COVID-19 patients at risk of severe illness will be covered by the federal government. The corresponding therapeutic products are listed in the Annex to the Epidemics Ordinance.
Science Task Force advisory mandate to end on 31 March
The Science Task Force's advisory mandate will end earlier than scheduled at the end of March at its own request. The current advisory mandate is limited until the end of May. In light of the positive developments, the need for scientific advice is changing. Individual members of the Science Task Force will continue to be available to the Federal Council and the Federal Administration for consultation.
Since spring 2020, the Science Task Force has offered its scientific expertise. The Federal Council thanks the task force members for their outstanding work. The guidance offered by the Science Task Force has been invaluable in managing the pandemic.
Address for enquiries
Federal Office of Public Health FOPH
www.bag.admin.ch
media@bag.admin.ch
COVID-19 Infoline +41 58 463 00 00
COVID-19 Vaccination Infoline +41 58 377 88 92
Source: https://www.bag.admin.ch/bag/en/home/das-bag/aktuell/medienmitteilungen.msg-id-87216.html
____________________________________________________________________________________
04.02.2022
Coronavirus: Entering Switzerland
On account of the COVID-19 pandemic, certain restrictions are in place for entering Switzerland. Anyone who has not been vaccinated or recovered from COVID must present a negative test result on entering Switzerland. In addition, anyone entering by air or long-distance bus (coach) must complete an entry form.
- Notice for foreign nationals
- Entry form
- Test requirement
- Quarantine requirement
- Which COVID-19 vaccines allow entry to Switzerland?
- Can I enter with a foreign certificate?
- Contact details of the cantonal authorities
- Entering with children
- Distancing and hygiene rules in Switzerland
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Notice for foreign nationals
You may not be allowed to enter Switzerland. Before you travel, you should check the following:
- Am I even allowed to travel to Switzerland?You’ll find the answer to this question on the website of the State Secretariat for Migration (SEM) as the SEM is responsible for Switzerland’s entry requirements.
- Only if entry is permitted: what rules are there?You’ll find the answer to this on the FOPH website as the Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH) is responsible for health-related measures at the border.
Anyone who has a Swiss passport or a valid Swiss residence permit can enter Switzerland at any time. All travellers must take note of the health-related measures at the Swiss border.
The interactive travel check tool shows you what measures apply to you.
Below you’ll find a simplified overview of the current health-related measures at the border. Nevertheless, please read carefully the chapters on the individual measures on this page.
Entry form
If you intend to enter Switzerland by air or long-distance bus (coach) you must present a completed entry form. This also applies to people who have been vaccinated or have recovered from COVID.
Please note that the entry form can be completed at the earliest 48h before entry.
What to do:
Fill out the electronic entry form on a computer or smartphone before you enter Switzerland. As soon as you have filled out the online form, you’ll be emailed a QR code as confirmation. Keep this code handy for inspection when you arrive in Switzerland. During these checks, you can show the QR code on your smartphone or a printed confirmation. If you have not filled out the entry form despite the obligation to do so, the controlling authority can punish you with a CHF 100 fine. The same applies if you provide false information on the form.
Exemptions from obligation to complete an entry form
Information for passenger transport companies
You'll find plenty of information in the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs). For example you'll find information on what to do if you don’t have a seat number or if there are technical problems and about data protection.
Test requirement
You have been fully vaccinated or have recovered from COVID and can prove this with a valid COVID certificate? Then you are exempt from the test requirement on boarding and on entry to Switzerland. If you are entering Switzerland by air or long-distance bus (coach), you must nevertheless first complete an entry form.
Note that the airline or long-distance bus company can nevertheless demand a test on boarding. For this reason you should find out directly from the airline or long-distance bus company what rules they apply.
You have not been fully vaccinated or recovered from COVID? Then you are subject to the test requirement on boarding and on entry to Switzerland.
- Test at boarding:People aged 16 and over intending to enter Switzerland by air or long-distance bus (coach) must be able to show the negative result of a PCR test (performed no more than 72 hours prior to boarding)or a rapid antigen test (performed no more than 24 hours previously). If you cannot show such a test you will not be allowed to board the aircraft or vehicle. Note: For people entering Switzerland from a country with a variant of concern, the test requirement on boarding already applies to those aged 6 and over.
Exception to the test requirement on boarding
- Test on entry: On entering Switzerland, people aged 16 and over who have not been vaccinated or recovered from COVID and over must be able to show the negative result of a PCR test (performed no more than 72 hours prior to entry)or arapid antigen test (performed no more than 24 hours previously). Anyone unable to present a valid negative test on entry must expect to be fined and must take the test in Switzerland.
Exceptions to the general test requirement
You'll find plenty of information in the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs).
Quarantine requirement
There are currently no countries on the list of
countries with a variant of concern. There is thus no quarantine requirement for people arriving in Switzerland at present.
It is the list of countries with a variant of concern that determines whether you have to go into quarantine after entering Switzerland. Anyone who has been in a country with a variant of concern in the 10 days prior to entering Switzerland must go into quarantine. This also applies to people who have been vaccinated or have recovered from COVID.
People entering Switzerland from a country that is not on the list of countries with a variant of concern do not have to go into quarantine after entry.
Exceptions to the quarantine requirement
Which COVID-19 vaccines allow entry to Switzerland?
People who have received one of the following vaccines can enter Switzerland:
- Pfizer/BioNTech (BNT162b2 / Comirnaty® / Tozinameran)
- Moderna (mRNA-1273 / Spikevax / COVID-19 vaccine Moderna)
- AstraZeneca (AZD1222 Vaxzevria®/ Covishield™)
- Janssen / Johnson & Johnson (Ad26.COV2.S)
- Sinopharm / BIBP (SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine (Vero Cell))
- Sinovac (CoronaVac)
- COVAXIN®
- Novavax (NVX-CoV2373 / Nuvaxovid™/ CovovaxTM)
People who have been vaccinated with two different vaccines are considered to be fully vaccinated if:
- the vaccines used have been approved by the authorities in Switzerland (Swissmedic) and the EU (EMA) or are on the WHO emergency use list and
- they were administered in accordance with the regulations or recommendations of the state in which the vaccination took place.
Vaccination must be documented in the form of a recognised certificate or other proof of vaccination. In addition to your last name, first name and date of birth, the proof of vaccination must also include the date of vaccination and the vaccine used.
Please note: not all vaccines that allow entry to Switzerland also entitle you to enter places with a COVID certificate requirement in Switzerland (e.g. restaurants).
Do you have a valid EU Digital COVID Certificate (EU-DCC)? This is valid in Switzerland. Did you recover or were you vaccinated abroad and do not have an EU-DCC? In this case, you can apply for a Swiss COVID certificate. You’ll find everything you need to know on the page Where and how to get a COVID certificate and how long it is valid.
Can I enter with a foreign certificate?
Yes. The certificates from EU/EFTA countries and those issued by third countries and regions that are connected to the EU system can also be used to enter Switzerland. Please note that you must still observe the mandatory testing requirement on arrival, and that the certificate alone does not entitle you to enter the country.
Switzerland recognises certificates from the following countries and regions:
- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Cabo Verde
- El Salvador
- Faroe Islands
- Georgia
- Holy See
- Israel
- Lebanon
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Morocco
- New Zealand
- North Macedonia
- Panama
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Singapore
- Taiwan (Chinese Taipei)
- Thailand
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- Uruguay
Contact details of the cantonal authorities
If after entering Switzerland you must go into travel quarantine, notify the canton responsible accordingly within two days of entry.
Canton | Contact details |
Aargau | |
Appenzell Ausserrhoden | |
Appenzell Innerrhoden | |
Basel-Landschaft | |
Basel-Stadt | |
Bern | |
Fribourg | |
Geneva | |
Glarus | |
Graubünden | |
Jura | |
Lucerne | |
Neuchâtel | |
Nidwalden | |
Obwalden | |
St. Gallen | |
Schaffhausen | |
Schwyz | |
Solothurn | |
Thurgau | |
Ticino | |
Uri | |
Valais | |
Vaud | |
Zug | |
Zurich | |
Principality of Liechtenstein |
Entering with children
If you are entering Switzerland with children or adolescents, please note the following:
- The entry form obligation also applies to children and adolescents of all ages who enter Switzerland by air or long-distance bus (coach). They can be included in the entry form of an adult travelling with them.
- The quarantine requirement after entering Switzerland from countries with a variant of concern also applies to children and adolescents of all ages, even if they have been vaccinated or have recovered from COVID.
- Children under 16 are exempt from the test requirement unless they are entering Switzerland from a country with a variant of concern. In this case they must have a test before boarding an aircraft or bus as well as after entering Switzerland.
Distancing and hygiene rules in Switzerland
On the Measures and Ordinances page you will see what rules and bans apply on a nationwide basis. In other words, these coronavirus-related measures at the very least apply all over Switzerland; the cantons may have stricter measures. This means you should also find out from the canton to which you are travelling what rules apply there.
Please also observe the distancing and hygiene rules that apply in Switzerland. This is the best way to protect yourself and others from infection with the coronavirus.
Have you started to have symptoms of illness after entering Switzerland? Take them seriously and follow the instruction on the Isolation and Quarantine page.
______________________________________________________________________________
25.01.2022
EU Digital COVID Certificates
Information on 'EU Digital COVID Certificates' in Switzerland
Certificates from EU/EFTA countries and those issued by non-member states that are connected to the EU system can be used to enter Switzerland. Covid certificates are required to access indoor public spaces such as restaurants, cultural events and leisure activities, and public transportation. Switzerland's different regions can implement specific territorial regulations.
Please consult the Measures section for further details. Travellers are advised to carry their ceritifcates at all times.
The 'EU Digital COVID Certificate' (EUDCC) is digital proof, valid in all EU countries, that a person has either been vaccinated against COVID-19, has recovered from COVID-19, or has received a negative test result. National authorities are responsible for issuing the certificate. All EU citizens and their family members, as well as non-EU nationals who are legally staying or residing in an EU country and have the right to travel within the EU, can get the EUDCC. A list of non-EU countries and territories whose certificates are accepted under the same conditions as the EUDCC is also available.
Note: although the 'EU Digital COVID Certificate' is valid across the EU, countries remain responsible for their own entry rules and health measures during the pandemic. This means that entry requirements depend on your destination.
As of 1 February 2022, vaccination certificates will be valid for travel purposes within the EU for a period of 9 months (270 days).
What are the rules to enter this country from an EU Member State or Schengen Associated country?
Document checklist
1. All travellers entering Switzerland, including vaccinated and recovered persons, must complete the Entry Form at least 48 hours before departure.
2. Persons over the age of 16, who are not vaccinated or recovered, must provide a negative PCR test (no older than 72 hours before arrival), or a negative antigen test (no older than 24 hours before arrival).
3. From 31 January, the validity period of all vaccination certificates is 270 days.
Entry rules
- Persons who are fully vaccinated or have recovered from COVID-19 are exempt from all testing requirements when entering Switzerland.
- Currently, there are no countries of variant concern on the mandatory quarantine list.
- Travellers are reminded to consult the lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration to check their national status for entry.
Entering this country with the EU Digital COVID certificate
For holders of the EUDCC:
- Vaccines authorised by Swissmedic and the European Medicines Agency are recognised as valid for 270 days (from 31 January). Holders of vaccines authorised by the WHO emergency list are eligible to apply for a Swiss COVID certificate.
- Persons who have been vaccinated or have recovered from COVID-19 are no longer required to present a negative PCR test or antigen test before entry into Switzerland.
- Persons over the age of 16, and who are not vaccinated or recovered, must provide a negative PCR test (no older than 72 hours before arrival), or a negative antigen test (no older than 24 hours before arrival).
In addition:
- All travellers, including vaccinated and recovered persons, must complete the Entry Form at least 48 hours before departure.
- Currently, there are no countries of variant concern on the mandatory quarantine list. However, travellers are reminded to consult the lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration to check their national status for entry.
Entering this country without the EU Digital COVID certificate or with a certificate not compliant with national requirements
Documents equivalent to the 'EU Digital COVID Certificate' (EUDCC) are also accepted, if they meet the same requirements listed above for the EUDCC.
Currently, there are no countries of variant concern on the mandatory quarantine list. However, travellers are reminded to consult the lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration to check their national status for entry.
Learn more:
Federal Office of Public Health
State Secretariat for Migration
What are the rules to enter this country from outside an EU Member State or Schengen Associated country?
Entry rules
- Persons who are fully vaccinated or have recovered from COVID-19 are exempt from all testing requirements when entering Switzerland.
- Persons over the age of 16 who are not vaccinated or recovered must provide a negative PCR test (no older than 72 hours before arrival), or a negative antigen test (no older than 24 hours before arrival). They are also required to take a second test between the 4th and 7th days of their arrival and submit the results to the relevant cantonal authority.
- Currently, there are no countries of variant on Switzerland's mandatory quarantine list.
- Travellers are reminded to consult the lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration to check their national status for entry.
Mandatory documents
- All travellers, including vaccinated and recovered persons, must complete the pre-departure Entry Form at least 48 hours before departure.
- Vaccines authorised by Swissmedic and the European Medicines Agency are recognised as valid for 270 days. Holders of vaccines authorised by the WHO emergency list are eligible to apply for a Swiss COVID certificate.
Learn more:
Federal Office of Public Health
State Secretariat for Migration
What are the rules if I go abroad from this country, and when I return from abroad?
To learn about specific conditions to go abroad and return to Switzerland depending on your country of departure, fill in the Entry Form at least 48 hours before departure.
Currently, there are no countries of variant concern on the mandatory quarantine list. However, travellers are reminded to consult the lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration to check their national status for entry.
May I transit this country?
Travellers in transit, including air/bus/train passengers, must complete the Entry Form. If they choose to leave the airport, or their bus or train, they are required to take a PCR test.
Otherwise, the standard rules apply to travel between and from without EU and Schengen-area countries.
General measures
The Federal Council provides an explanation of the national rules in place. Be aware that specific cantonal rules may apply. Telecommuting is advised.
Use of facemasks
Facemasks must be worn in all indoor venues and wherever groups of people congregate. Exceptions to the the rule include persons who cannot wear coverings for medical reasons.
Physical Distancing
Physical distancing of 1.5 metres between persons is advised.
Indoor and outdoor meetings, public or private gatherings and events
Certificates are required for entry, facemasks must be worn and social distancing rules should be respected.
A maximum of 30 persons can attend an indoor event. If more than 10 persons are gathered, access should be limited to guests with certificates. The rule outdoors is a maximum of 50 persons.
Safety measures for public transportation
Passengers over age 12 must wear facemasks or respirators when aboard public transportation.
Places of worship
Churches are open and religious events can be held. Certificates are required for entry where more than 50 persons are in attendance. Facemasks must be worn and social distancing rules respected.
Quarantine
There are currently no countries of variant on the mandatory quarantine list. However, travellers from outside the EU/Schengen area are reminded to consult lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration to check their national status for entry.
Learn more:
Federal Office of Public Health
Non-essential (other than medicine and food) shops
Travellers in transit, including air/bus/train passengers, must complete the Entry Form. If they choose to leave the airport, or their bus or train, they are required to take a PCR test.
Otherwise, the standard rules apply to travel between and from without EU and Schengen-area co
All shops are open. Facemasks must be worn and social distancing rules respected.
Tourist accommodations
Tourist accommodations are open. Certificates are required for entry. Facemasks must be worn and social distancing rules respected.
Catering establishments
Catering establishments, restaurants, bars and night clubs where beverages and food are consumed are restricted to holders of COVID certificates. Facemasks must be worn and social distancing rules should be respected.
A maximum of 30 persons wearing facemasks are allowed in each indoor venue. The rule for outdoor venues is 50 persons.
Cinemas, museums and indoor attractions
Cultural, leisure and sports facilities are open. Certificates are required for entry. Facemasks must be worn and social distancing rules should be respected.
Personal care services
Personal care services are open by appointment. Certificates are required for entry. Facemasks must be worn and social distancing rules should be respected.
Outdoors areas and beaches
Outdoor exercise is enouraged. Wherever groups of people congregate, and if social distancing rules cannot be observed, facemasks should be worn.
Ski facilities
Ski areas (e.g. transport installations with ski slopes) may open if authorised by each canton.
Operators implement strict precautionary measures, including the mandatory wearing of facemasks in both the transport installations and the waiting areas for these installations.
National website with coronavirus-related information for TOURISM
Useful Info for tourists
See: www.myswitzerland.com;
www.bag.admin.ch
______________________________________________________________________
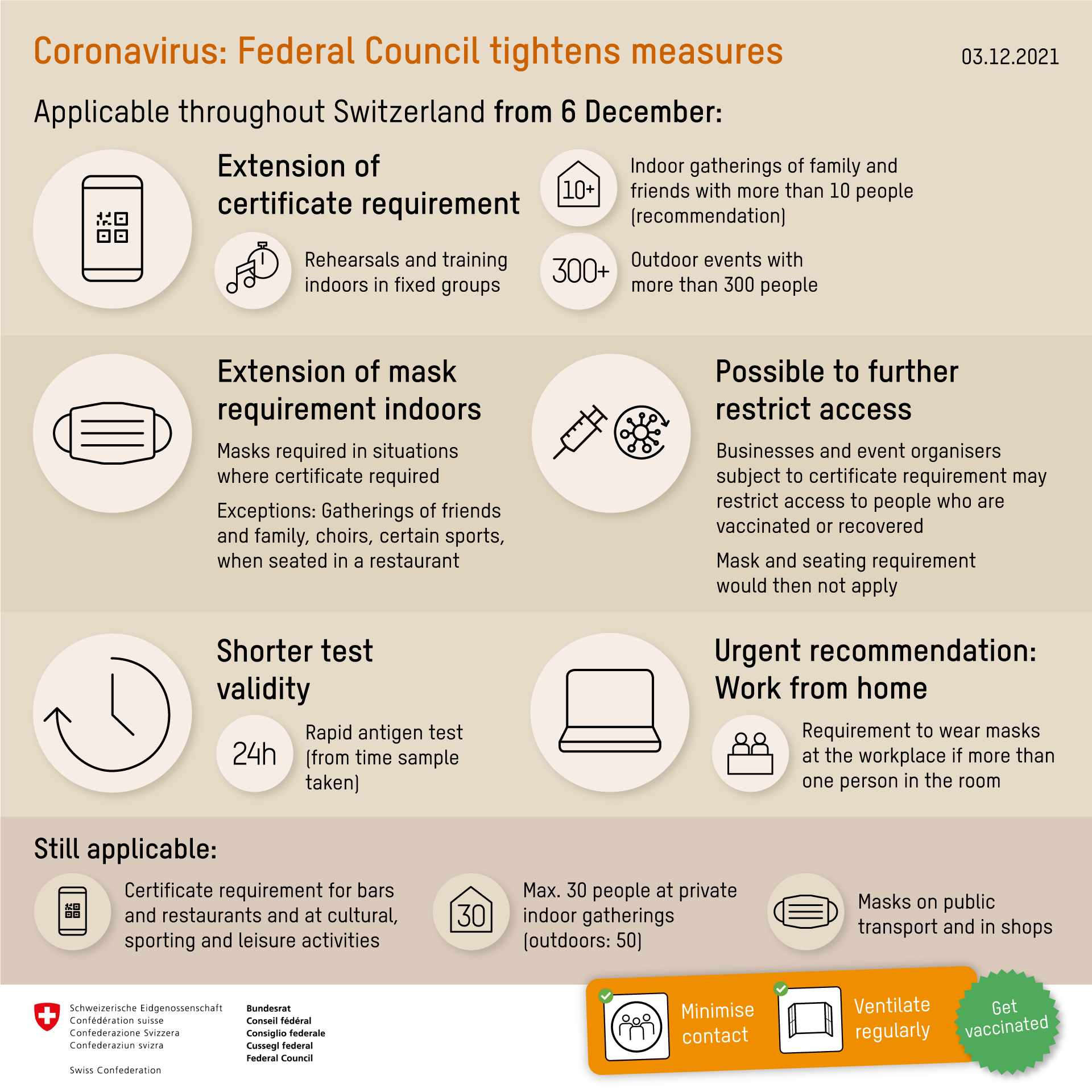
06.12.2021
What are the rules to enter this country from an EU Member State or Schengen Associated country?
All travellers over the age of 16 entering Switzerland, including vaccinated and recovered persons, must be in possession of a negative PCR test (less than 72 hours before arrival) and also complete the Entry Form. There are exceptions to this rule for passengers in transit and those entering Switzerland on urgent medical grounds.
A second test (PCR test or rapid antigen test) must be carried out between the fourth and seventh day of entry.
Entering this country with the EU Digital COVID certificate
All travellers over the age of 16 entering Switzerland, including vaccinated and recovered persons, must be in possession of a negative PCR test (less than 72 hours before arrival) and also complete the Entry Form. There are exceptions to this rule for passengers in transit and those entering Switzerland on urgent medical grounds.
A second test (PCR test or rapid antigen test) must be carried out between the fourth and seventh day of entry.
Vaccines authorised by Swissmedic and the European Medicines Agency are recognised and valid for one year. Holders of vaccines authorised by the WHO emergency list are eligible to apply for a Swiss COVID certificate.
Learn more:
Federal Office of Public Health
State Secretariat for Migration
Entering this country without the EU Digital COVID certificate or with a certificate not compliant with national requirements
All travellers over the age of 16 entering Switzerland, including vaccinated and recovered persons, must be in possession of a negative PCR test (less than 72 hours before arrival) and also complete the Entry Form. There are exceptions to this rule for passengers in transit and those entering Switzerland on urgent medical grounds.
A second test (PCR test or rapid antigen test) must be carried out between the fourth and seventh day of entry.
Vaccines authorised by Swissmedic and the European Medicines Agency are recognised and valid for one year. Holders of vaccines authorised by the WHO emergency list are eligible to apply for a Swiss COVID certificate.
Learn more:
Federal Office of Public Health
State Secretariat for Migration
Documents you need to travel in Europe
Health cover for temporary stays
What are the rules to enter this country from outside an EU Member State or Schengen Associated country?
All travellers over the age of 16 entering Switzerland, including vaccinated and recovered persons, must be in possession of a negative PCR test (less than 72 hours before arrival) and also complete the Entry Form. There are exceptions to this rule for passengers in transit and those entering Switzerland on urgent medical grounds.
A second test (PCR test or rapid antigen test) must be carried out between the fourth and seventh day of entry.
Vaccines authorised by Swissmedic and the European Medicines Agency are recognised and valid for one year. Holders of vaccines authorised by the WHO emergency list are eligible to apply for a Swiss COVID certificate.
Switzerland has ended quarantine requirements for countries of variant concern. Travellers are advised to consult lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration to check thier national entry status.
Learn more:
What are the rules to enter this country from outside an EU Member State or Schengen Associated country?
All travellers over the age of 16 entering Switzerland, including vaccinated and recovered persons, must be in possession of a negative PCR test (less than 72 hours before arrival) and also complete the Entry Form. There are exceptions to this rule for passengers in transit and those entering Switzerland on urgent medical grounds.
A second test (PCR test or rapid antigen test) must be carried out between the fourth and seventh day of entry.
Vaccines authorised by Swissmedic and the European Medicines Agency are recognised and valid for one year. Holders of vaccines authorised by the WHO emergency list are eligible to apply for a Swiss COVID certificate.
Switzerland has ended quarantine requirements for countries of variant concern. Travellers are advised to consult lists maintained by the Federal Office of Public Health and the State Secretariat for Migration to check thier national entry status.
Learn more:
Federal Office of Public Health
State Secretariat for Migration
May I transit this country?
Passengers in transit are exempt from the requirement to provide the PCR test on entry. However, they must still fill in the Entry Form and provide proof of their vaccinated, recovered or negative status.
Learn more:
Federal Office of Public Health
State Secretariat for Migration
What are the rules if I go abroad from this country, and when I return from abroad?
All travellers over the age of 16 entering Switzerland, including vaccinated and recovered persons, must be in possession of a negative PCR test (less than 72 hours before arrival) and also complete the Entry Form. There are exceptions to this rule for passengers in transit and those entering Switzerland on urgent medical grounds.
A second test (PCR test or rapid antigen test) must be carried out between the fourth and seventh day of entry.
Learn more:
Federal Office of Public Health
State Secretariat for Migration
May I fly to this country?
You can find the latest information on air travel regulations for this country on the IATA website.
You can also find information about air passenger rights on our portal for citizens.
General measures
The Federal Council provides an explanation of the national rules in place. Be aware that specific cantonal rules may apply. Telecommuting is advised.
Use of facemasks
Masks must be worn at all indoor and many outdoor events.
Physical Distancing
Face masks and social distancing are recommended.
Indoor and outdoor meetings, public or private gatherings and events
Access to indoor and outdoor events for people over 16 is restricted to holders of a valid COVID certificate.
There are exceptions for religious ceremonies, funerals, events that fall within the scope of the normal activities and services of public authorities, political events and self-help groups with up to 50 people. For these indoor events, masks must be worn, the consumption of food and drinks is banned, and contact details must be collected.
Safety measures for public transportation
Hygiene protocols are in place. Passengers over the age of 12 have to wear masks on Swiss public transport.
Places of worship
OPEN WITH LIMITATIONS
Religious events and funeral ceremonies with fewer than 50 people are exempt from COVID certificate requirements. Guests must wear face masks and provide their contact details.
Quarantine
Isolation
Anyone who tests positive for the coronavirus must self-isolate. Details can be found on the Isolation and quarantine page.
Quarantine
Individuals must go into quarantine if they have:
- been in close contact with someone who has tested positive (exceptions for vaccinated or recovered individuals are possible). Details can be found on the Isolation and quarantine page.
- travelled to Switzerland from areas with a concerning virus variant to Switzerland and are neither vaccinated against COVID-19 nor recovered from COVID-19. Details can be found on the Entering Switzerland page.
Non-essential (other than medicine and food) shops
OPEN WITH LIMITATIONS
All shops are open. There are no restrictions on opening hours for service businesses.
Tourist accommodations
OPEN WITH LIMITATIONS
Tourist accommodations are open.
Catering establishments
OPEN WITH LIMITATIONS
Bars and restaurants are open. However, a maximum of 30 people wearing face masks are allowed indoors. The rule indoors is 50 people.
Cinemas, museums and indoor attractions
OPEN WITH LIMITATIONS
For indoor cultural and sporting activities, access for people aged 16 and over must be restricted to holders of a valid COVID certificate (the people required to have a certificate also include those leading a group). In addition, the premises must have effective ventilation.
Personal care services
COVID certificates are required for entrance.
Outdoors areas and beaches
OPEN
Access to indoor and outdoor events for people over 16 is restricted to holders of a valid COVID certificate.
Ski facilities
OPEN WITH LIMITATIONS
Ski areas (e.g. transport installations with ski slopes) may only be opened if authorised by the canton. The criteria for a canton to grant authorisation include, in particular, the availability of the necessary capacity in healthcare facilities and an epidemiological situation that permits the opening of the ski areas. Operators of ski areas must implement stringent precautionary measures, including the mandatory wearing of masks in both the transport installations and the waiting areas for these installations. The closure of restaurant businesses also applies in ski areas.
Federal Office of Public Health
State Secretariat for Migration
May I transit this country?
Passengers in transit are exempt from the requirement to provide the PCR test on entry. However, they must still fill in the Entry Form and provide proof of their vaccinated, recovered or negative status.
Learn more:
Federal Office of Public Health
State Secretariat for Migration
What are the rules if I go abroad from this country, and when I return from abroad?
All travellers over the age of 16 entering Switzerland, including vaccinated and recovered persons, must be in possession of a negative PCR test (less than 72 hours before arrival) and also complete the Entry Form. There are exceptions to this rule for passengers in transit and those entering Switzerland on urgent medical grounds.
A second test (PCR test or rapid antigen test) must be carried out between the fourth and seventh day of entry.
Learn more:
Federal Office of Public Health
State Secretariat for Migration
May I fly to this country?
You can find the latest information on air travel regulations for this country on the IATA website.
You can also find information about air passenger rights on our portal for citizens.
General measures
The Federal Council provides an explanation of the national rules in place. Be aware that specific cantonal rules may apply. Telecommuting is advised.
Use of facemasks
Masks must be worn at all indoor and many outdoor events.
Physical Distancing
Face masks and social distancing are recommended.
Indoor and outdoor meetings, public or private gatherings and events
Access to indoor and outdoor events for people over 16 is restricted to holders of a valid COVID certificate.
There are exceptions for religious ceremonies, funerals, events that fall within the scope of the normal activities and services of public authorities, political events and self-help groups with up to 50 people. For these indoor events, masks must be worn, the consumption of food and drinks is banned, and contact details must be collected.
Safety measures for public transportation
Hygiene protocols are in place. Passengers over the age of 12 have to wear masks on Swiss public transport.
Places of worship
OPEN WITH LIMITATIONS
Religious events and funeral ceremonies with fewer than 50 people are exempt from COVID certificate requirements. Guests must wear face masks and provide their contact details.
Quarantine
Isolation
Anyone who tests positive for the coronavirus must self-isolate. Details can be found on the Isolation and quarantine page.
Quarantine
Individuals must go into quarantine if they have:
- been in close contact with someone who has tested positive (exceptions for vaccinated or recovered individuals are possible). Details can be found on the Isolation and quarantine page.
- travelled to Switzerland from areas with a concerning virus variant to Switzerland and are neither vaccinated against COVID-19 nor recovered from COVID-19. Details can be found on the Entering Switzerland page.
Non-essential (other than medicine and food) shops
OPEN WITH LIMITATIONS
All shops are open. There are no restrictions on opening hours for service businesses.
Tourist accommodations
OPEN WITH LIMITATIONS
Tourist accommodations are open.
Catering establishments
OPEN WITH LIMITATIONS
Bars and restaurants are open. However, a maximum of 30 people wearing face masks are allowed indoors. The rule indoors is 50 people.
Cinemas, museums and indoor attractions
OPEN WITH LIMITATIONS
For indoor cultural and sporting activities, access for people aged 16 and over must be restricted to holders of a valid COVID certificate (the people required to have a certificate also include those leading a group). In addition, the premises must have effective ventilation.
Personal care services
COVID certificates are required for entrance.
Outdoors areas and beaches
OPEN
Access to indoor and outdoor events for people over 16 is restricted to holders of a valid COVID certificate.
Ski facilities
OPEN WITH LIMITATIONS
Ski areas (e.g. transport installations with ski slopes) may only be opened if authorised by the canton. The criteria for a canton to grant authorisation include, in particular, the availability of the necessary capacity in healthcare facilities and an epidemiological situation that permits the opening of the ski areas. Operators of ski areas must implement stringent precautionary measures, including the mandatory wearing of masks in both the transport installations and the waiting areas for these installations. The closure of restaurant businesses also applies in ski areas.
National website with coronavirus-related information for TOURISM
Useful Info for tourists
See: www.myswitzerland.com;
www.bag.admin.ch
Source: Re-open EU (europa.eu)
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
04.12.2021
Coronavirus: list of countries with a variant of concern
The list was updated on 4 December 2021. Currently there are no countries on the list of countries with a variant of concern.
The newly added countries are written in bold in the respective list.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland from 04.12.21
Countries and regions with a variant of concern
Currently there are no countries on the list of countries with a variant of concern. The previous countries were removed from the list as of 4 December.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland between 30.11.21 and 03.12.21
__________________________________
03.12.2021
________________________________________________________
30.11.2021
The newly added countries are written in bold in the respective list.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland from 30.11.21
Countries* and regions with a variant of concern
- Angola
- Australia
- Belgium
- Botswana
- Canada
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Egypt
- Eswatini
- Hong Kong
- Israel
- Japan
- Lesotho
- Malawi
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- Nigeria
- Portugal
- South Africa
- United Kingdom
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
* The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland on 29.11.21
___________________________________________________________________________________________
29.11.2021
Coronavirus: list of countries with a variant of concern
The list was updated on 29 November 2021. Due to a new virus variant, countries are again on the list of countries with a variant of concern.
- Explanation of the list
- List of countries with a variant of concern
- How is this different from the SEM list?
The newly added countries are written in bold in the respective list.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland
Countries* with a variant of concern
From 26 November 2021, 20h00
- Belgium
- Botswana
- Eswatini
- Hong Kong
- Israel
- Lesotho
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- South Africa
- Zimbabwe
From 27 November 2021, 20h00
- Czech Republic
- Egypt
- Malawi
- Netherlands
- United Kingdom
From 29 November 2021, 00h00
- Angola
- Australia
- Denmark
- Zambia
From 30 November 2021, 00h00
- Canada
- Japan
- Nigeria
- Portugal
* The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland between 04.08.21 and 25.11.21
Have you stayed in a country with a variant of concern and are now entering Switzerland? On the page Entering Switzerland, you can find out which requirements you have to observe.
__________________________________________________________________________________________-
26.11.2021
Tightening of entry rules: quarantine for arrivals
Since 8pm on 26.11.2021, various countries have been on the list of countries with a variant of concern. Anyone entering Switzerland from these countries must present a negative test result and quarantine for 10 days. This also applies to vaccinated and recovered persons.
Only people who are Swiss nationals or hold a residence permit for Switzerland or a country in the Schengen area can enter Switzerland from these countries.
The newly added countries are written in bold in the respective list.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland from 26.11.21, from 20h00
Countries* with a worrying variant
- Belgium
- Botswana
- Czech Republic
- Egypt
- Eswatini
- Hong Kong
- Israel
- Lesotho
- Malawi
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Netherlands
- South Africa
- United Kingdom
- Zimbabwe
* The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland between 4.8.21 - 25.11.21
__________________________________________
08.09.2021
Ordinances
Ordinance 3 on Measures to Combat the Coronavirus (COVID-19)
Ordinance on Measures during the Special Situation to combat the COVID-19 Epidemic
Ordinance on the Proximity Tracing System for the Sars-CoV-2 coronavirus
Ordinance on Measures to Combat the Coronavirus (COVID-19) in International Passenger Transport
Notice for foreign nationals
You may not be allowed to enter Switzerland. Before you travel, you should check the following:
- Am I even allowed to travel to Switzerland? You’ll find the answer to this question on the website of the State Secretariat for Migration (SEM) as the SEM is responsible for Switzerland’s entry requirements.
- Only if entry is permitted: what rules are there? You’ll find the answer to this on the FOPH website as the Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH) is responsible for health-related measures at the border. Please also note the section Additional information for incoming persons.
Further information: https://www.bag.admin.ch/bag/en/home/krankheiten/ausbrueche-epidemien-pandemien/aktuelle-ausbrueche-epidemien/novel-cov/empfehlungen-fuer-reisende/quarantaene-einreisende.html
_____________________________________________________________________
10.08.2021
As of 4 August 2021, there are no longer any countries on the list of countries with a variant of concern. There is currently no quarantine obligation for people entering Switzerland. Therefore, some cantons have temporarily deactivated their quarantine notification form.
Coronavirus: Entering Switzerland
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic there are special rules for people entering Switzerland. Depending on the type of travel, you might have to fill out an entry form, show proof of a negative test and/or go into quarantine.
Notice for foreign nationals
You may not be allowed to enter Switzerland. Before you travel, you should check the following:
- Am I even allowed to travel to Switzerland? You’ll find the answer to this question on the website of the State Secretariat for Migration (SEM) as the SEM is responsible for Switzerland’s entry requirements.
- Only if entry is permitted: what rules are there? You’ll find the answer to this on the FOPH website as the Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH) is responsible for health-related measures at the border. Please also note the section Additional information for incoming persons.
Anyone who has a Swiss passport or a valid Swiss residence permit can enter Switzerland at any time.
All travellers must take note of the health-related measures at the Swiss border. The interactive travel check tool shows you what measures apply to you.
Here you’ll find a simplified overview of the current health-related measures at the border:
Graphic_Measures_Entry (PDF, 2 MB, 28.06.2021)
You will find information on the individual rules in the relevant sections of this page:
- COVID-19 vaccination requirements
- Entering Switzerland with the EU certificate
- Entry form
- Negative test result
- Quarantine
- Entering with children
- Additional information for incoming persons
COVID-19 vaccination requirements
People who are fully vaccinated are exempt from many health-related measures at the border. These exemptions apply to people who have been vaccinated with one of the following vaccines:
- Pfizer/BioNTech (BNT162b2 / Comirnaty® / Tozinameran)
- Moderna (mRNA-1273 / Spikevax / COVID-19 vaccine Moderna)
- AstraZeneca (AZD1222 Vaxzevria®/ Covishield™)
- Janssen / Johnson & Johnson (Ad26.COV2.S)
- Sinopharm / BIBP (SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine (Vero Cell))
- Sinovac (CoronaVac)
Do you not have a COVID certificate that is recognised in Switzerland? In this case, in addition to your last name, first name and date of birth, your proof of vaccination must also include the date of vaccination and the vaccine used.
The exemptions to the health-related measures at the border apply for twelve months from the time that you are fully vaccinated.
Entering Switzerland with the EU certificate
The “EU Digital COVID Certificate” of the EU is also recognised in Switzerland. You can thus enter Switzerland with the certificate.
Entry form
You will find the entry form for incoming travellers at swissplf.admin.ch. Fill out the form before you enter Switzerland.
Who has to fill out the entry form?
You must complete the form if the following applies to you:
- You are entering Switzerland by airplane. This also includes a stopover in Switzerland, for example air travellers who have to change flight.
Filling out and control
Fill out the electronic entry form on a computer or smartphone before or during travel. Once you’ve filled out the form you’ll be emailed a QR code as confirmation. Have this code ready for inspection when you enter Switzerland. If you are controlled you can show the QR code on your smartphone or produce a printed confirmation. If you have not filled out the entry form despite the obligation to do so, the controlling authority can punish you with a CHF 100 fine. The same applies if you provide false information on the form.
What do you do if you don’t have internet access to fill out the form?
Further information on the entry form
You'll find plenty of information in the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs). For example you'll find information on what to do if you don’t have a seat number or if there are technical problems, about data protection and about the paper version of the form.
Do you have questions that aren’t answer in the FAQs? You can call the infoline on +41 58 464 44 88 from 6am to 11pm, 7 days a week. You’ll find information on the costs of the call on the Contact information and links page.
Negative test result
Are you not fully vaccinated or unable to prove that you have recovered from COVID-19 in the last 6 months? In the following cases you will have to present proof of a negative PCR test (not older than 72 hours) or rapid antigen test (not older than 48 hours):
- You are entering Switzerland by airplane.
- Within the last 10 days before entering Switzerland, you have been in a place with a variant of concern.
We recommend that you get tested after your arrival in Switzerland. This applies even if you have no symptoms. You can find more information on the page Tests.
Quarantine for persons arriving in Switzerland
Have you been in a country with a variant of concern in the last 10 days before entering Switzerland? If you have not been vaccinated or are unable to prove that you have recovered from COVID-19 in the last 6 months, you must go into quarantine after entering Switzerland.
What to do after entering Switzerland
- Upon arrival, go immediately to your home or to other suitable accommodation (e.g. a hotel or holiday apartment). On the way there, keep a minimum distance of 1.5 metres from other people. If you are unable to maintain this distance, we recommend that you wear a mask. Avoid public transport if possible.
- Report your arrival to the cantonal authority responsible within two days.
- For 10 days after your arrival in Switzerland you must stay in your home or other suitable accommodation without going out. Avoid contact with other people and follow the instructions in the document instructions on quarantine (PDF, 343 kB, 01.07.2021). This document is also available in the languages of the migrant population.
- There is the possibility of shortening travel quarantine from day 7 onwards. You’ll find information on the Isolation and Quarantine site.
The cantonal authorities are responsible for monitoring quarantine, and they conduct spot checks. Anyone who fails to comply with the quarantine requirement is committing an offence under the Epidemics Act (in German), which can be punished by a fine of up to CHF 10,000.
Further information on quarantine
You'll find more information on travel quarantine in the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ). There you’ll find answers to questions on things like continued payment of salary and loss of earnings during quarantine.
Do you still have questions that aren’t answered in the FAQs? You can call the infoline on +41 58 464 44 88 from 6am to 11pm, 7 days a week. You’ll find information on the costs of the call on the Contact information and links page.
Contact details of the cantonal authorities
Contact the competent cantonal authority within two days of your arrival.
| Canton | Contact details |
|---|---|
| Aargau | Online application form (In German) |
| Appenzell Ausserrhoden | Online application form (In German) |
| Appenzell Innerrhoden | Homepage (In German) |
| Basel-Landschaft | Homepage (In German) |
| Basel-Stadt | Homepage (In German) |
| Bern | Online application form (In German) |
| Fribourg | Homepage (In German) |
| Geneva | Online application form (In French) |
| Glarus | |
| Graubünden | |
| Jura | |
| Lucerne | Homepage (In German) |
| Neuchâtel | Homepage (In French) |
| Nidwalden | Online application form (In German) |
| Obwalden | |
| St. Gallen | Online application form (In German) |
| Schaffhausen | +41 52 632 70 01 |
| Schwyz | Online application form (In German) |
| Solothurn | Homepage (In German) |
| Thurgau | Online Application Form (In German) |
| Ticino | Homepage (in Italian) |
| Uri | Online application form (In German) |
| Valais | Online application form |
| Vaud | Homepage (in French) |
| Zug | Online application form (In German) |
| Zurich | Online application form |
| Principality of Liechtenstein | Homepage (in German) |
Entering with children
The rules for entering Switzerland also apply to children and adolescents, with the exception of the testing requirement. If you are entering Switzerland with children or adolescents, please note the following:
- The entry form obligation also applies to children and adolescents of all ages. They can be included in the entry form of an adult travelling with them.
- The quarantine obligation also applies to children and adolescents of all ages.
- Children under the age of 16 are never required to provide proof of a negative coronavirus test on entering Switzerland. They are exempt from the test requirement on boarding and from the test requirement at the Swiss border.
Additional information for incoming persons
On the Measures and Ordinances page you will see what rules and bans apply on a nationwide basis. In other words, these coronavirus-related measures at the very least apply all over Switzerland; the cantons may have stricter measures. This means you should also find out from the canton to which you are travelling what rules apply there.
Please also observe the distancing and hygiene rules that apply in Switzerland. This is the best way to protect yourself and others from infection with the coronavirus.
Have you started to have symptoms of illness after entering Switzerland? Take them seriously and follow the instruction on the Isolation and Quarantine page.
Further information: https://www.bag.admin.ch/bag/en/home/krankheiten/ausbrueche-epidemien-pandemien/aktuelle-ausbrueche-epidemien/novel-cov/empfehlungen-fuer-reisende/quarantaene-einreisende.html#489451312
Source: European Union/Re-open EU
04.08.2021
You may not be allowed to enter Switzerland. Before you travel, you should check the following:
- Am I even allowed to travel to Switzerland? You’ll find the answer to this question on the website of the State Secretariat for Migration (SEM) as the SEM is responsible for Switzerland’s entry requirements.
- Only if entry is permitted: what rules are there? You’ll find the answer to this on the FOPH website as the Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH) is responsible for health-related measures at the border. Please also note the section Additional information for incoming persons.
Anyone who has a Swiss passport or a valid Swiss residence permit can enter Switzerland at any time.
Travelcheck
The Travelcheck allows you to check whether and under what conditions you can enter Switzerland.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland from 4.8.21
Countries with a variant of concern
Currently there are no countries on the list of countries with a variant of concern. India, Nepal and the UK were removed from the list with effect 4 August.
You will find information on the individual rules in the relevant sections of this page:
- COVID-19 vaccination requirements
- Entering Switzerland with the EU certificate
- Entry form
- Negative test result
- Quarantine
- Additional information for incoming persons
_____________________________________________________________________________
21.07.2021
The newly added countries are written in bold in the respective list.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland from 26.6.21
Countries* with a worrying variant
- India
- Nepal
- United Kingdom
* The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 17.6.21 and 25.6.21
1. Countries*
- Andorra
- Argentina
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Cabo Verde
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Egypt
- Georgia
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Maldives
- Mexico
- Mongolia
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- Paraguay
- Seychelles
- Slovenia
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- Uruguay
2. Countries* with a worrying variant
- Brazil
- Canada
- India
- Nepal
- South Africa
- United Kingdom
* The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
3. Areas of neighbouring countries
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Pays de la Loire
No longer on the list from 17.6.21: Estonia
Older lists can be found in the corresponding version of the “COVID-19 Ordinance on International Passenger Transport Measures”. Access to all versions of this ordinance can be gained in the classified compilation (listed on the right-hand side in a box).
What are the rules to enter this country from an EU Member State or Schengen Associated country?
Entering by air:
All travellers entering Switzerland by air need to fill the entry form swissplf.admin.ch.
This also includes a stopover in Switzerland, for example air travellers who have to change flight.
The entry form must also be filled out for children. They can be included in the form of an adult travelling with them.
Further requirements depend on whether you want to enter with or without EU Digital COVID Certificate. Please take in consideration that from 8 July 2021, the European Commission adopted a decision recognizing Swiss COVID-19 certificates as equivalent to the EU Digital COVID Certificate.
Entering this country with the EU Digital COVID certificate
This country is ready to connect to the EU Digital COVID certificate Gateway
The Federal Office of Public Health provides a regularly updated list of countries defined as COVID-19 risk area, so called countries or areas with variants of concern.
Entering by car/coach/train:
If you are travelling from a country or area without a variant of concern you can enter Switzerland without any further pandemic-related measures and you are therefore exempt from the test and quarantine requirement. For more info please use the Swiss Travelcheck tool.
Entering by air:
Holders of ‘EU Digital COVID Certificates’ (EUDCC) entering Switzerland from countries without a variant of concern can enter without being subject to additional restriction if their certificate contains one of the following:
- Certificate of vaccination, which is valid in accordance with the following conditions:
Start of validity:
- for two-dose vaccination (Comirnaty®, COVID-19 Vaccine Moderna, AstraZeneca, Sinopharm BIBP, Sinovac, Covishield™): on the day of administration of the second dose;
- for single-dose vaccination (Janssen): on the 22nd day after administration of the dose.
- for individuals with prior confirmed Sars-CoV-2 infection:
- on the day of administration of the single dose of a two-dose vaccination (Comirnaty®, COVID-19 Vaccine Moderna, AstraZeneca, Sinopharm BIBP, Sinovac, Covishield™)
- on the 22nd day after administration of a single-dose vaccination (Janssen).
Duration of validity: 365 days from the date of administration of the last dose.
Persons who have been vaccinated are persons who have received a vaccine that:
- is authorised in Switzerland and which has been administered in full in accordance with the recommendations of the Federal Office of Public Health of Switzerland;
- has been authorised by the European Medicines Agency for the European Union and has been administered in full in accordance with the requirements or recommendations of the country in which the vaccination was administered; or
- is authorised under the WHO Emergency Use Listing and has been administered in full in accordance with the requirements or recommendations of the country in which the vaccination was administered
- Certificate of recovery from COVID-19 from the 11th day after the positive test result and lasts for 180 days from the date of the test result.
- a pre-departure PCR test (taken within 72 hours prior to arrival) or a rapid antigen test (taken within 48 hours prior to arrival).
Children under the age of 16 are never required to provide proof of a negative coronavirus test on entering Switzerland. They are exempt from the test requirement on boarding and from the test requirement at the Swiss border.
Holders of EUDCC who have not been vaccinated or recovered from COVID-19 and who have been in a country or area with a variant of concern in the last 10 days before entering Switzerland must go into quarantine after entering Switzerland. The quarantine requirement also applies to children even if the parents are fully vaccinated.
There is the possibility of shortening travel quarantine from day 7 onwards.
Find out more:
Entering Switzerland (admin.ch)
Exemptions to the testing and quarantine requirement
Exemptions to the entry form requirement
National use of COVID certificate (admin.ch)
Entering this country without the EU Digital COVID certificate or with a certificate not compliant with national requirements
The Federal Office of Public Health provides a regularly updated list of countries defined as COVID-19 risk area, so called countries or areas with variants of concern.
Entry into Switzerland is also possible without a Covid certificate, whereby the following entry conditions must be considered:
Entering by car/coach/train:
If you are travelling from a country or area without a variant of concern you can enter Switzerland without any further pandemic-related measures and you are therefore exempt from the test and quarantine requirement. For more info please fill the Travel check questionnaire.
Entering by air:
Test requirement
Travellers who are not fully vaccinated or unable to prove that they have recovered from COVID-19 in the last 6 months will have to present proof of a negative PCR test (max. 72 hours old) or rapid antigen test (max. 48 hours old) in the following cases:
- If they are entering Switzerland by airplane.
- If they have been, within the last 10 days before entering Switzerland, in a country with a variant of concern.
Children under the age of 16 are never required to provide proof of a negative coronavirus test on entering Switzerland. They are exempt from the test requirement on boarding and from the test requirement at the Swiss border.
Quarantine requirement
Travellers who have been in a country with a variant of concern in the last 10 days before entering Switzerland and who have not been vaccinated according to the requirements of the Swiss authorities or are unable to prove that they have recovered from COVID-19 in the last 6 months must go into quarantine after entering Switzerland.
The quarantine requirement also applies to children– even if the parents are fully vaccinated.
There is the possibility of shortening travel quarantine from day 7 onwards.
Proof of vaccination
Persons who have been vaccinated are persons who have received a vaccine that:
- is authorised in Switzerland and which has been administered in full in accordance with the recommendations of the Federal Office of Public Health of Switzerland;
- has been authorised by the European Medicines Agency for the European Union and has been administered in full in accordance with the requirements or recommendations of the country in which the vaccination was administered; or
- is authorised under the WHO Emergency Use Listing and has been administered in full in accordance with the requirements or recommendations of the country in which the vaccination was administered.
The vaccination is regarded as being effective for 12 months from the date on which it was administered in full; the Janssen vaccine is regarded as being effective for 12 months from the 22nd day after it was administered in full.
Proof of vaccination may be provided in the form that is customary at the time. In addition to the surname, forename and date of birth of the person concerned, it must include the following information:
- the date of vaccination;
- the vaccine used.
Proof of recovery
Proof of recovery remains valid for 6 months from the 11th day following confirmation of the infection.
Proof of recovery may be provided in the form that is customary at the time. In addition to the surname, forename and date of birth of the person concerned, it must include the following information:
- confirmation of the infection including the name and address of the confirming body (test centre, doctor, pharmacy, hospital);
- confirmation that isolation has been terminated or confirmation from a doctor of recovery.
Find out more:
Rules for entering Switzerland
What to do after entering Switzerland
Exemptions to the testing and quarantine requirement
Exemptions to the entry form requirement
Documents you need to travel in Europe
Health cover for temporary stays
What are the rules to enter this country from outside an EU Member State or Schengen Associated country?
Entry from non high-risk countries (as listed here)
Entry to Switzerland is possible provided that the normal entry requirements are met when crossing the border (e.g. valid visa and travel document).
Entry from high-risk countries
Entry from a high-risk country (that is not listed here) is possible if one of the following criteria, as well as the normal entry requirements are met:
- You have Swiss citizenship.
- You hold a travel document (e.g. a passport or identity card) and:
- a Swiss residence permit (L B C Ci permit);
- a cross-border permit (G permit),
- an FDFA legitimation card;
- a D visa issued by Switzerland;
- a C visa issued by Switzerland after 16 March 2020 in a valid exceptional case or in order to work on a short-term contract;
- an assurance of a residence permit
- a confirmation of notification for the cross-border provision of services up to 90 days in any calendar year (e.g. UK nationals).
- You hold a refugee’s or stateless person’s travel document issued by Switzerland, a passport for foreign nationals issued by Switzerland, a valid residence or permanent residence permit or an F-Permit.
- You have rights of free movement. If you require a visa, a valid Schengen C-visa, a valid D-visa or a valid Schengen residence permit are sufficient.
- You are in a situation of special necessity (see below). The border control authority will assess the necessity of the situation.
- You can prove that they have been vaccinated with a recognised vaccine
- You are under 18 and are travelling with an adult who has been fully vaccinated.
- You are simply travelling directly through Switzerland with the intention and possibility of entering another country.
You must be able to prove that you meet the abovementioned requirements. Suitable documentary proof must be produced at the border or when you apply for a visa.
Find out more Information: Corona: Questions and answers on entry and stay in Switzerland, the exceptions and suspension of visas (admin.ch)
Independent of the above-mentioned entry-requirements, health-related measures at the border may apply (see «What are the rules to enter this country from an EU Member State or Schengen Associated country?”)
Rules for entering Switzerland
The Federal Office of Public Health provides a regularly updated list of countries defined as COVID-19 risk area, so called countries or areas with variants of concern.
The entry form for incoming travellers can be found at swissplf.admin.ch.
The form must be filled out by all travellers entering Switzerland by airplane. This also includes a stopover in Switzerland, for example air travellers who have to change flight.
The entry form must also be filled out for children. They can be included in the form of an adult travelling with them.
Travellers who are not fully vaccinated or unable to prove that they have recovered from COVID-19 in the last 6 months will have to present proof of a negative PCR test (max. 72 hours old) or rapid antigen test (max. 48 hours old) in the following cases:
- If they are entering Switzerland by airplane.
- If they have been, within the last 10 days before entering Switzerland, in a country with a variant of concern.
Children under the age of 16 are never required to provide proof of a negative coronavirus test on entering Switzerland. They are exempt from the test requirement on boarding and from the test requirement at the Swiss border.
In addition, travellers who have been in a country with a variant of concern in the last 10 days before entering Switzerland and who have not been vaccinated according to the requirements of the Swiss authorities or are unable to prove that they have recovered from COVID-19 in the last 6 months must go into quarantine after entering Switzerland.
The quarantine requirement also applies to children even if the parents are fully vaccinated.
There is the possibility of shortening travel quarantine from day 7 onwards.
Proof of vaccination
Persons who have been vaccinated are persons who have received a vaccine that:
- is authorised in Switzerland and which has been administered in full in accordance with the recommendations of the Federal Office of Public Health of Switzerland;
- has been authorised by the European Medicines Agency for the European Union and has been administered in full in accordance with the requirements or recommendations of the country in which the vaccination was administered; or
- is authorised under the WHO Emergency Use Listing and has been administered in full in accordance with the requirements or recommendations of the country in which the vaccination was administered.
The vaccination is regarded as being effective for 12 months from the date on which it was administered in full; the Janssen vaccine is regarded as being effective for 12 months from the 22nd day after it was administered in full.
Proof of vaccination may be provided in the form that is customary at the time. In addition to the surname, forename and date of birth of the person concerned, it must include the following information:
- the date of vaccination;
- the vaccine used.
Proof of recovery
Proof of recovery remains valid for 6 months from the 11th day following confirmation of the infection.
Proof of recovery may be provided in the form that is customary at the time. In addition to the surname, forename and date of birth of the person concerned, it must include the following information:
- confirmation of the infection including the name and address of the confirming body (test centre, doctor, pharmacy, hospital);
- confirmation that isolation has been terminated or confirmation from a doctor of recovery.
Find out more:
Rules for entering Switzerland
What to do after entering Switzerland
Exemptions to the testing and quarantine requirement
Exemptions to the entry form requirement
May I transit this country?
Partially
Passengers in transit, such as air travellers who have to change their flight, must complete an entry form before a stopover in Switzerland.If they continue their journey by train they have to present a negative COVID-19 test upon entry.
Additionally, the following rules apply:
Transit from a Schengen state to other Schengen state
Entry from a Schengen state for the purpose of travelling on to another Schengen state is possible for anyone who is lawfully present in the Schengen area.
Transit from a Schengen state to a third country
Entry from a Schengen state for the purpose of travelling on to a state outside the Schengen area is possible for anyone who is lawfully present in the Schengen area.
Transit from a third country considered by the SEM to be high-risk to a Schengen state
Third-country citizens holding a residence document or a visa type D for their destination country in the Schengen area are permitted to travel through Switzerland to that country.
The normal requirements for entering Switzerland apply.
It is only possible to enter Switzerland from a high-risk country in order to travel on to another Schengen state for a short stay of up to 90 days if you can prove that you have been vaccinated (see “How can I prove that I am vaccinated?”). Persons under 18 may enter Switzerland if they are travelling with an adult who has been vaccinated.
Otherwise the normal requirements for entering Switzerland apply.
If you have not been vaccinated, but your destination country in the Schengen area has authorised your entry for a short stay of up to 90 days, you may only enter the Schengen area by travelling directly to your destination country (i.e. you may not travel though Switzerland).
Transit from a third country not considered by the SEM to be high-risk to a Schengen state
When entering Switzerland from a third country that is not considered high-risk in order to travel on to another Schengen state, the normal requirements for entering Switzerland apply.
Transit from a third country considered by the SEM to be high-risk to another third country
It is not possible to enter Switzerland from a third country that is considered high-risk in order to travel on to another country outside the Schengen area, unless transiting through Zurich or Geneva airport. Travellers should check whether they require a transit visa. In such cases, travellers do not actually enter Switzerland but remain in the transit area of the airport.
Transit visa requirements: Passport and visa requirements not depending on citizenship (PDF, 337 kB, 18.03.2021)
Transit from a third country not considered by the SEM to be high-risk to another third country
Entry into Switzerland from a third country which is not on the SEM high-risk list for onward travel to another country outside the Schengen area is possible subject to the normal entry and transit requirements (N.B. a transit visa may be required).
General measures
The latest measures in place in Switzerland are available at measures and ordinances
Use of facemasks
Masks must be worn in indoor public spaces, for example in shops, in restaurants, on public transport. Further details can be found on the Masks page.
Physical Distancing
Physical distancing of a minimum of 1.5 metres is required (if not possible: recommendation to wear a face mask).
Indoor and outdoor meetings, public or private gatherings and events
Certificates (for use in Switzerland such as large-scale events)
Vaccination certificates
Start of validity:
- for two-dose vaccination (Comirnaty®, COVID-19 Vaccine Moderna, AstraZeneca, Sinopharm BIBP, Sinovac, Covishield™): on the day of administration of the second dose;
- for single-dose vaccination (Janssen): on the 22nd day after administration of the dose;
- for individuals with prior confirmed Sars-CoV-2 infection:
- on the day of administration of the single dose of a two-dose vaccination (Comirnaty®, COVID-19 Vaccine Moderna, AstraZeneca, Sinopharm BIBP, Sinovac, Covishield™),
- on the 22nd day after administration of the single dose of a single-dose vaccination (Janssen)..
Duration of validity: 365 days from the date of administration of the last dose.
Certificate of recovery from COVID-19 valid from the 11th day after the positive test result for 180 days from the date of the test result.
PCR test (valid for 72 hours after sample taking) or a rapid antigen test (valid for 48 hours after sample taking).
People under age 16 do not need a COVID certificate.Find out more:
National use of COVID certificate (admin.ch)
Events with a certificate: no masks, no restrictions
Large-scale events with more than 1,000 people may only be attended by people with a valid COVID certificate. In addition, the organisers of large-scale events must obtain authorisation from the cantonal authority. Furthermore, for nightclubs, discos or events involving dancing the COVID certificate is mandatory. There will be no restrictions on events at which access is limited to people with a COVID certificate, including large-scale events.
Events without a COVID certificate requirement
The rule for events without a COVID certificate requirement are as follows:
- If the public are seated, up to 1000 people may attend indoors or outdoors.
- If people are standing or moving around, up to 250 people may attend indoors, and up to 500 outdoors.
- Up to two-thirds of the venue’s capacity may be used indoors or outdoors.
- Indoors: masks must be worn in areas where food and drink are served, and food and drink may only be consumed in the designated areas; contact details must be recorded if seated.
- Outdoors: no requirement to wear masks.
- Events and concerts involving dancing are not allowed.
Private gatherings: 30 people indoors, 50 outdoors
The limits regarding private events continue to apply, i.e. no more than 30 people indoors and 50 people outdoors.
Trade fairs: no capacity restrictions
The ban on trade fairs for fewer than 1000 people indoors is to be lifted. Cantonal authorisation is required for fairs over 1’000 visitors a day. Capacity restrictions for trade fairs will also be lifted regardless of the number of visitors or the restriction to people with a COVID certificate.
nformation on Tourism at National level
National website with coronavirus-related information for TOURISM
Useful Info for tourists
See: www.myswitzerland.com;
www.bag.admin.ch
____________________________________________________________________
23.06.2021
Further information : https://www.bag.admin.ch/bag/en/home/das-bag/aktuell/medienmitteilungen.msg-id-84127.html
16.06.2021
Notice for foreign nationals
You may not be allowed to enter Switzerland. Before you travel, you should check the following:
- Am I even allowed to travel to Switzerland? You’ll find the answer to this question on the website of the State Secretariat for Migration (SEM) as the SEM is responsible for Switzerland’s entry requirements.
- Only if entry is permitted: what rules are there? You’ll find the answer to this on the FOPH website as the Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH) is responsible for health-related measures at the border. Please also note the section Additional information for incoming tourists.
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold in the respective list.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland from 17.6.21
1. Countries*
- Andorra
- Argentina
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Cabo Verde
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Egypt
- Georgia
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Maldives
- Mexico
- Mongolia
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- Paraguay
- Seychelles
- Slovenia
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- Uruguay
2. Countries* with a worrying variant
- Brazil
- Canada
- India
- Nepal
- South Africa
- United Kingdom
* The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
3. Areas of neighbouring countries
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Pays de la Loire
No longer on the list from 17.6.21: Estonia
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 3.6.21 and 16.6.21
1. Countries*
- Andorra
- Argentina
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Cabo Verde
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Egypt
- Estonia
- Georgia
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Maldives
- Mexico
- Mongolia
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- Paraguay
- Seychelles
- Slovenia
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- Uruguay
2. Countries* with a worrying variant
- Brazil
- Canada
- India
- Nepal
- South Africa
- United Kingdom
* The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
3. Areas of neighbouring countries
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Pays de la Loire
No longer on the list since 3.6.21: Croatia, Cyprus, France: Région Occitanie and Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur, Germany: Land Sachsen and Thüringen, Iran (Islamic Republic of), Italy: Regione Campania and Puglia, Luxembourg, Turkey
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 27.5.21 and 2.6.21
28.05.2021
Coronavirus: Measures and ordinances
Notice for foreign nationals
You may not be allowed to enter Switzerland. Before you travel, you should check the following:
- Am I even allowed to travel to Switzerland? You’ll find the answer to this question on the website of the State Secretariat for Migration (SEM) as the SEM is responsible for Switzerland’s entry requirements.
- Only if entry is permitted: what rules are there? You’ll find the answer to this on the FOPH website as the Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH) is responsible for health-related measures at the border.
Coronavirus: Entering Switzerland
As of 6 p.m. on 27 May, the UK is on the FOPH list of risk countries.
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold in the respective list.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland from 27.5.21
1. Countries*
- Andorra
- Argentina
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Cabo Verde
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Egypt
- Estonia
- Georgia
- Iran (Islamic Republic of)
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Maldives
- Mexico
- Mongolia
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- Paraguay
- Seychelles
- Slovenia
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- Turkey
- Uruguay
2. Countries* with a worrying variant
- Brazil
- Canada
- India
- Nepal
- South Africa
- United Kingdom (from 27 May, 6 p.m.)
* The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
3. Areas of neighbouring countries
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Campania
- Regione Puglia
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 20.5.21 and 26.5.21
1. Countries*
- Andorra
- Argentina
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Cabo Verde
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Egypt
- Estonia
- Georgia
- Iran (Islamic Republic of)
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Maldives
- Mexico
- Mongolia
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- Paraguay
- Seychelles
- Slovenia
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- Turkey
- Uruguay
2. Countries* with a worrying variant
- Brazil
- Canada
- India
- Nepal
- South Africa
* The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
3. Areas of neighbouring countries
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Campania
- Regione Puglia
No longer on the list since 20.5.2021: Austria: Land Oberösterreich and Land Salzburg, France: Région Bretagne and Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine, Hungary, Italy: Regione Basilicata, Palestinian territory (Occupied), Poland, Qatar, Serbia.
14.05.2021
Coronavirus: Entering Switzerland
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic there are special rules for people entering Switzerland. Depending on the type of travel, you might have to fill out an entry form, show proof of a negative test and/or go into quarantine.
New rules starting 17 May 2021
For travellers entering Switzerland from a state or area where a Sars-CoV-2 variant of concern is prevalent, the exemptions from the testing and quarantine requirements will be limited.
Entry form
06.05.2021
Coronavirus: Entering Switzerland
FOPH list of risk countries
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold in the respective list.
As of 6 p.m. on 3 May, Nepal is on the FOPH list of risk countries.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland from 17.5.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Oberösterreich
- Land Salzburg
France:
- Région Bretagne
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Basilicata
- Regione Campania
- Regione Puglia
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Argentina
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Brazil
- Cabo Verde
- Canada
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Egypt
- Estonia
- Georgia
- Hungary
- India
- Iran (Islamic Republic of)
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Maldives
- Mexico
- Mongolia
- Nepal
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- Palestinian territory (Occupied)
- Paraguay
- Poland
- Qatar
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- Turkey
- Uruguay
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 6.5.21 and 16.5.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Oberösterreich
- Land Salzburg
France:
- Région Bretagne
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Campania
- Regione Puglia
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Argentina
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Brazil
- Cabo Verde
- Canada
- Chile
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Egypt
- Estonia
- Hungary
- India
- Kuwait
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Mexico
- Nepal
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- Palestinian territory (Occupied)
- Paraguay
- Poland
- Qatar
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- Turkey
- Uruguay
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
No longer on the list since 6.5.2021: Armenia, Austria: Land Burgenland, Land Kärnten, Land Niederösterreich and Land Wien, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Czechia, Greece, Italy: Regione Emilia Romagna, Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia and Regione Toscana, Jordan, Kosovo, Lebanon, Montenegro, North Macedonia, San Marino, Ukraine.
27.04.2021
Coronavirus: Entering Switzerland
FOPH list of risk countries
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold in the respective list.
As of 6 p.m. on 26 April, India is on the FOPH list of risk countries.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland from 3.5.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Burgenland
- Land Kärnten
- Land Niederösterreich
- Land Oberösterreich
- Land Salzburg
- Land Wien
France:
- Région Bretagne
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Campania
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Puglia
- Regione Toscana
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Argentina
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brazil
- Bulgaria
- Cabo Verde
- Canada
- Chile
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Egypt
- Estonia
- Greece
- Hungary
- India
- Jordan
- Kosovo (Republic of)
- Kuwait
- Lebanon
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Mexico
- Montenegro
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- North Macedonia
- Palestinian territory (Occupied)
- Paraguay
- Poland
- Qatar
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- Uruguay
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 26.4.21 and 2.5.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Burgenland
- Land Kärnten
- Land Niederösterreich
- Land Oberösterreich
- Land Salzburg
- Land Wien
France:
- Région Bretagne
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Campania
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Puglia
- Regione Toscana
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brazil
- Bulgaria
- Canada
- Chile
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Greece
- Hungary
- India (from 26 April, 6 p.m.)
- Jordan
- Kosovo (Republic of)
- Kuwait
- Lebanon
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Montenegro
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- North Macedonia
- Palestinian territory (Occupied)
- Paraguay
- Poland
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- Uruguay
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 22.4.21 and 25.4.21
No longer on the list since 22.4.2021: Austria: Land Steiermark, Italy: Regione Lazio, Italy: Regione Liguria, Italy: Regione Marche, Italy: Regione Veneto, Latvia, Maldives, Malta, Moldova, Monaco, Peru, Romania, Slovakia.
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Burgenland
- Land Kärnten
- Land Niederösterreich
- Land Oberösterreich
- Land Salzburg
- Land Wien
France:
- Région Bretagne
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Campania
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Puglia
- Regione Toscana
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brazil
- Bulgaria
- Canada
- Chile
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Greece
- Hungary
- Jordan
- Kosovo (Republic of)
- Kuwait
- Lebanon
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Montenegro
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- North Macedonia
- Palestinian territory (Occupied)
- Paraguay
- Poland
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- Uruguay
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 19.4.21 and 21.4.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Burgenland
- Land Kärnten
- Land Niederösterreich
- Land Oberösterreich
- Land Salzburg
- Land Steiermark
- Land Wien
France:
- Région Bretagne
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Campania
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Lazio
- Regione Liguria
- Regione Marche
- Regione Puglia
- Regione Toscana
- Regione Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brazil
- Bulgaria
- Canada
- Chile
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Greece
- Hungary
- Jordan
- Kosovo (Republic of)
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Maldives
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- North Macedonia
- Palestinian territory (Occupied)
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Poland
- Romania
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- Uruguay
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
12.04.2021
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland from 19.4.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Burgenland
- Land Kärnten
- Land Niederösterreich
- Land Oberösterreich
- Land Salzburg
- Land Steiermark
- Land Wien
France:
- Région Bretagne
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Campania
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Lazio
- Regione Liguria
- Regione Marche
- Regione Puglia
- Regione Toscana
- Regione Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brazil
- Bulgaria
- Chile
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Greece
- Hungary
- Jordan
- Kosovo (Republic of)
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Maldives
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- North Macedonia
- Palestinian territory (Occupied)
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Poland
- Romania
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- Uruguay
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 8.4.21 and 18.4.21
No longer on the list since 8.4.2021: Albania, France: Région Corse, Italy: Regione Abruzzo, Italy: Regione Basilicata, Italy: Regione Molise, Italy: Regione Umbria, Israel, Jamaica, United Arab Emirates.
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Burgenland
- Land Kärnten
- Land Niederösterreich
- Land Oberösterreich
- Land Salzburg
- Land Steiermark
- Land Wien
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Campania
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Lazio
- Regione Liguria
- Regione Marche
- Regione Toscana
- Regione Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brazil
- Bulgaria
- Chile
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Greece
- Hungary
- Jordan
- Kosovo (Republic of)
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Luxembourg
- Maldives
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- North Macedonia
- Palestinian territory (Occupied)
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Poland
- Romania
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- Ukraine
- Uruguay
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 5.4.21 and 7.4.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Burgenland
- Land Kärnten
- Land Niederösterreich
- Land Oberösterreich
- Land Salzburg
- Land Steiermark
- Land Wien
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Corse
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Abruzzo
- Regione Basilicata
- Regione Campania
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Lazio
- Regione Liguria
- Regione Marche
- Regione Molise
- Regione Toscana
- Regione Umbria
- Regione Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Albania
- Andorra
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brazil
- Bulgaria
- Chile
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Greece
- Hungary
- Israel
- Jamaica
- Jordan
- Kosovo (Republic of)
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Luxembourg
- Maldives
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- North Macedonia
- Palestinian territory (Occupied)
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Poland
- Romania
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- United Arab Emirates
- Ukraine
- Uruguay
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
31.03.2021
FOPH list of risk countries
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold in the respective list.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland from 5.4.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Burgenland
- Land Kärnten
- Land Niederösterreich
- Land Oberösterreich
- Land Salzburg
- Land Steiermark
- Land Wien
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Corse
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Abruzzo
- Regione Basilicata
- Regione Campania
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Lazio
- Regione Liguria
- Regione Marche
- Regione Molise
- Regione Toscana
- Regione Umbria
- Regione Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Albania
- Andorra
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brazil
- Bulgaria
- Chile
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Greece
- Hungary
- Israel
- Jamaica
- Jordan
- Kosovo (Republic of)
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Luxembourg
- Maldives
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- North Macedonia
- Palestinian territory (Occupied)
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Poland
- Romania
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- United Arab Emirates
- Ukraine
- Uruguay
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
25.03.2021
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 25.3.21 and 4.4.21
No longer on the list since 25.3.2021: Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, France: Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine, Italy: Regione Puglia, Ireland, Lithuania, Qatar, Saint Lucia, United Kingdom, United States of America.
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Burgenland
- Land Kärnten
- Land Niederösterreich
- Land Oberösterreich
- Land Salzburg
- Land Steiermark
- Land Wien
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Corse
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Abruzzo
- Regione Basilicata
- Regione Campania
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Lazio
- Regione Liguria
- Regione Marche
- Regione Molise
- Regione Toscana
- Regione Umbria
- Regione Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Albania
- Andorra
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Brazil
- Bulgaria
- Chile
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Hungary
- Israel
- Jordan
- Kosovo (Republic of)
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Luxembourg
- Maldives
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- North Macedonia
- Palestinian territory (Occupied)
- Peru
- Poland
- Romania
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Sweden
- United Arab Emirates
- Uruguay
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland from 5.4.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Burgenland
- Land Kärnten
- Land Niederösterreich
- Land Oberösterreich
- Land Salzburg
- Land Steiermark
- Land Wien
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Corse
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Abruzzo
- Regione Basilicata
- Regione Campania
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Lazio
- Regione Liguria
- Regione Marche
- Regione Molise
- Regione Toscana
- Regione Umbria
- Regione Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Albania
- Andorra
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brazil
- Bulgaria
- Chile
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Greece
- Hungary
- Israel
- Jamaica
- Jordan
- Kosovo (Republic of)
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Luxembourg
- Maldives
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- North Macedonia
- Palestinian territory (Occupied)
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Poland
- Romania
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Sweden
- Tanzania
- United Arab Emirates
- Ukraine
- Uruguay
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 25.3.21 and 4.4.21
No longer on the list since 25.3.2021: Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, France: Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine, Italy: Regione Puglia, Ireland, Lithuania, Qatar, Saint Lucia, United Kingdom, United States of America.
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Burgenland
- Land Kärnten
- Land Niederösterreich
- Land Oberösterreich
- Land Salzburg
- Land Steiermark
- Land Wien
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Corse
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Abruzzo
- Regione Basilicata
- Regione Campania
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Lazio
- Regione Liguria
- Regione Marche
- Regione Molise
- Regione Toscana
- Regione Umbria
- Regione Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Albania
- Andorra
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Brazil
- Bulgaria
- Chile
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Hungary
- Israel
- Jordan
- Kosovo (Republic of)
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Luxembourg
- Maldives
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- North Macedonia
- Palestinian territory (Occupied)
- Peru
- Poland
- Romania
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Sweden
- United Arab Emirates
- Uruguay
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
22.03.2021
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 22.3.21 and 24.3.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Burgenland
- Land Kärnten
- Land Niederösterreich
- Land Oberösterreich
- Land Salzburg
- Land Steiermark
- Land Wien
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Corse
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Germany:
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Abruzzo
- Regione Basilicata
- Regione Campania
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Lazio
- Regione Liguria
- Regione Marche
- Regione Molise
- Regione Puglia
- Regione Toscana
- Regione Umbria
- Regione Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Albania
- Andorra
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahrain
- Barbados
- Belgium
- Brazil
- Bulgaria
- Chile
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Hungary
- Ireland
- Israel
- Jordan
- Kosovo (Republic of)
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Maldives
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands (Kingdom of the)
- North Macedonia
- Occupied Palestinian territory
- Peru
- Poland
- Qatar
- Romania
- Saint Lucia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Sweden
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States of America
- Uruguay
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
19.03.2021
Federal government measures to combat coronavirus
Next desicion expected on 14 April
Source: https://www.admin.ch/gov/en/start/documentation/media-releases.msg-id-82762.html
11.03.2021
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 11.3.21 and 21.3.21
Rules for entering Switzerland
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Kärnten
- Land Niederösterreich
- Land Salzburg
- Land Steiermark
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Italy:
- Regione Abruzzo
- Regione Campania
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Liguria
- Regione Marche
- Regione Molise
- Regione Puglia
- Regione Toscana
- Regione Umbria
Countries and areas*
- Albania
- Andorra
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahrain
- Barbados
- Brazil
- Chile
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Ireland
- Israel
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Maldives
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Kingdom of the Netherlands
- Peru
- Saint Lucia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Sweden
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States of America
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
No longer on the list since 11.3.2021: Portugal, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Spain.
08.03.2021
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 8.3.21 and 10.3.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Kärnten
- Land Niederösterreich
- Land Salzburg
- Land Steiermark
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
Italy:
- Regione Abruzzo
- Regione Campania
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Liguria
- Regione Marche
- Regione Molise
- Regione Puglia
- Regione Toscana
- Regione Umbria
Countries and areas*
- Albania
- Andorra
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahrain
- Barbados
- Brazil
- Chile
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Ireland
- Israel
- Kuwait
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Maldives
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Kingdom of the Netherlands
- Peru
- Portugal
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Spain
- Sweden
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States of America
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
25.02.2021
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 25.2.21 and 7.3.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Salzburg
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Région Occitanie (Languedoc-Roussillon-Midi-Pyrénées)
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur
Italy:
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Marche
- Regione Puglia
- Regione Umbria
Countries and areas*
- Albania
- Andorra
- Bahrain
- Brazil
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Ireland
- Israel
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Lithuania
- Malta
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Kingdom of the Netherlands
- Portugal
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Spain
- Sweden
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States of America
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
No longer on the list since 25 February 2021: Colombia, Land Brandenburg (Germany), Land Sachsen-Anhalt (Germany), Land Thüringen (Germany), Panama.
10.02.2021
These rules apply to all people who are permitted to enter Switzerland. That means they also apply if you are Swiss and returning to Switzerland after being abroad. You will find information on the individual rules and requirements in the relevant sections of this site:
- Entry form
- Negative test result
- Quarantine
- Exemptions from the testing and quarantine requirement
- Additional information for incoming tourists
FOPH list of risk countries
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold in the respective list.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland from 22.2.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Salzburg
France:
- Région Centre-Val de Loire
- Région Hauts-de-France
- Région Île de France
- Région Normandie
- Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Région Occitanie
- Région Pays de la Loire
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur
Germany:
- Land Brandenburg
- Land Sachsen-Anhalt
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Marche
- Regione Puglia
- Regione Umbria
Countries and areas*
- Albania
- Andorra
- Bahrain
- Brazil
- Colombia
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Ireland
- Israel
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Lithuania
- Malta
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Kingdom of the Netherlands
- Panama
- Portugal
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- South Africa
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom of Great Britain
- United States of America
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 11.2.21 and 21.2.21 List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 1.2.21 and 10.2.21 List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 21.1.21 and 31.1.21 List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 15.1.21 and 20.1.21 List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 12.1.21 and 14.1.21 List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 7.1.21 and 12.1.21 List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 28.12.20 and 6.1.21
Older lists can be found in the corresponding version of the “COVID-19 Ordinance on International Passenger Transport Measures”. Access to all versions of this ordinance can be gained in the classified compilation (listed on the right-hand side in a box).
08.02.2021
The provisions regarding the entry form and the negative test result apply from Monday, 8 Feburary.
These rules apply to all people who are permitted to enter Switzerland. That means they also apply if you are Swiss and returning to Switzerland after being abroad. You will find information on the individual rules and requirements in the relevant sections of this site:
- Entry form
- Negative test result
- Quarantine
- Exemptions from the testing and quarantine requirement
- Additional information for incoming tourists
As of 8 February 2021, we will refer to this list as the “FOPH list of risk countries” and no longer the “Quarantine list”. This is because, in addition to the requirement to go into quarantine, the list will now define further rules in connection with entering Switzerland.
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold in the respective list.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland from 1.2.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Salzburg
France:
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Brazil
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Ireland
- Israel
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Lithuania
- Malta
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Kingdom of the Netherlands
- Panama
- Portugal
- San Marino
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- South Africa
- United Kingdom of Great Britain
- United States of America
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
29.01.2021
There are various measures, rules and bans in place on the basis of the epidemic. They all have the same goal: to contain the coronavirus. The Federal Council will adapt the national rules if necessary. In some cantons stricter rules apply.
- Overview: national rules and bans
- Measures to date
- Cantonal measures
- Ordinances
- Explanatory notes
- Covid-19 Act
News: Changes in the measures
At its meeting on 27 January, the Federal Council took a range of decisions to further contain and overcome the coronavirus pandemic:
- Federal government will pay for persons without symptoms to be tested
It is believed that more than half of COVID-19 infections are transmitted by people who do not display symptoms and are unaware that they actually have the virus. The federal government has therefore permitted the testing of asymptomatic persons from mid-December as a further precautionary measure, e.g. in care homes, hotels and in the workplace. It will now assume the costs in order to encourage such institutions to conduct rapid tests, and this can be done by their own staff. Negative test results do not have to be reported; if a person tests positive to a rapid test, they must undergo a PCR test and the result must be reported.
By extending the testing strategy, the government hopes that local outbreaks of the virus, for example in schools, can be identified and contained at an early stage. This is particularly important in view of the fact that new, more infectious strains of the coronavirus are currently spreading in Switzerland. In such cases, the federal government will now also assume the cost of testing people who do not display symptoms. The local canton must present a test plan to the Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH) containing details of where testing will take place, who will be tested, how often and the type of test to be used.
These amendments come into force on 28 January 2021.
- Quarantine rules modified Until now anyone who has come into contact with an infected person has had to go into quarantine for ten days. Under the new rules, a person may leave quarantine after seven days if after this time they have a negative result from an antigen rapid test or a PCR test (molecular biological analysis), and are authorised to do so by the local cantonal authorities. The person must pay for the test themselves and must wear a mask and continue to socially distance until the full ten days' quarantine is over, unless they remain at home (or in the place they are quarantining - holiday apartment, hotel etc.). If their test result is positive, they must isolate immediately.
- New rules for entering Switzerland
Reduced travel quarantine
The new test-and-release strategy also applies to persons arriving in Switzerland from a country or region with a high risk of infection.
Negative PCR test result
- Persons arriving in Switzerland from a country or region with a high risk of infection must present valid proof of a negative PCR test result that is no more than 72 hours old.
- All persons arriving by air even from a country that is not considered high risk must be able to show a negative PCR test result before boarding the plane.
Contact tracing extended
Until now, only the contact details of people arriving in Switzerland from a high-risk country or region have been recorded. From now on, all persons arriving from abroad by air, boat, bus or train must complete an online form on arrival. With this information, cases of infection can be identified more easily and transmission chains broken more rapidly.
As a result of the Federal Council's new quarantine and travel rules, amendments are required to the relevant COVID-19 ordinances. These will apply from 8 February 2021.
From 1 February anyone contravening the measures to fight the epidemic will be committing an offence; persons who fail to comply with the rules may be fined between 50 and 200 francs, depending on the offence. For example, anyone who does not wear a mask on public transport, in stations, at a bus or tram stop or in and immediately outside publicly accessible buildings may be fined. A fixed penalty may also be issued to persons attending banned events or holding an unpermitted private event.
From 1 February the federal government will also assume the cost of vaccinations carried out by pharmacists, on the same conditions as in vaccination centres. This means that the cantons can include pharmacies in their vaccination programmes.
22.01.2021
No longer on the list from 21 January 2021: Croatia; Denmark; Georgia; Luxembourg; Serbia.
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland from 1.2.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Austria:
- Land Salzburg
France:
- Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
- Land Thüringen
Italy:
- Regione Emilia Romagna
- Regione Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Regione Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Brazil
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Estonia
- Ireland
- Israel
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Lithuania
- Malta
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Kingdom of the Netherlands
- Panama
- Portugal
- San Marino
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- South Africa
- United Kingdom of Great Britain
- United States of America
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid for arrivals in Switzerland between 15.1.21 and 20.1.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
Italy:
- Region Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Croatia
- Denmark
- Georgia
- Ireland
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Montenegro
- Kingdom of the Netherlands
- Panama
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovenia
- Sweden
- South Africa
- United Kingdom of Great Britain
- United States of America
- Czechia
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
13.01.2021
New rules apply throughout Switzerland from 18.01.2021
Further information: https://www.bag.admin.ch/bag/en/home/das-bag/aktuell/medienmitteilungen.msg-id-81967.html
12.01.2021
New on the list as of 12 January 2021, 1 pm: Ireland.
No longer on the list since 7 january 2021: Belize, Italy: Region Friuli Venezia Giulia.
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold.
List valid updon arriving in Switzerland from 15.1.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
Italy:
- Region Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Croatia
- Denmark
- Georgia
- Ireland
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Montenegro
- Kingdom of the Netherlands
- Panama
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovenia
- Sweden
- South Africa
- United Kingdom of Great Britain
- United States of America
- Czechia
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland between 12.1.21 and 14.1.21
Note: This list is valid from 12 January 2021, 1 pm.
Areas of neighbouring countries
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
Italy:
- Region Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Croatia
- Georgia
- Ireland
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Montenegro
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovenia
- Sweden
- South Africa
- United Kingdom of Great Britain
- United States of America
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland between 7.1.21 and 12.1.21
Note: This list is valid until 12 January 2021, 12.59 pm.
Areas of neighbouring countries
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
Italy:
- Region Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Croatia
- Georgia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Montenegro
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovenia
- Sweden
- South Africa
- United Kingdom of Great Britain
- United States of America
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland between 28.12.20 and 6.1.21
Areas of neighbouring countries
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
Italy:
- Region Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Region Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Belize
- Croatia
- Georgia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Montenegro
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovenia
- Sweden
- South Africa
- United Kingdom of Great Britain
- United States of America
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
31.12.2020
List of countries and areas with an increased risk of infection
On covid19.admin.ch you will find a visualisation of the list on a world map.
No longer on the list from 19 december 2020: Austria: Land Kärnten, Austria: Land Salzburg, Austria: Land Steiermark, Austria: Land Upper Austria, French Poynesia, Hungary, Italy: Region Emilia Romagna, Jordan, North Macedonia, Poland, Portugal.
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold.
List valid updon arriving in Switzerland from 28.12.2020
Areas of neighbouring countries
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
Italy:
- Region Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Region Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Belize
- Croatia
- Georgia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Montenegro
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovenia
- Sweden
- South Africa
- United Kingdom of Great Britain
- United States of America
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
Who must go into quarantine?
People who have spent time in a country or area with an increased risk of infection and then enter Switzerland must go into quarantine. The countries and areas affected are set down in a list.
The mandatory quarantine requirement is governed by the list valid at the moment of entry into Switzerland.
Check the list that is valid on your entry into Switzerland. Were you in one of the countries or areas on the list at any point in the last 10 days before entry into Switzerland? If so, you are legally required to go into quarantine and report your arrival in Switzerland to the cantonal authorities. Follow the instructions under What to do after entering Switzerland.
A negative test result does not exempt you from the mandatory quarantine requirement or shorten the quarantine period. This is because a negative test result does not rule out an infection with the new coronavirus. You will find the biological explanation for this on the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) page.
However, various people are exempt from the quarantine requirement in Switzerland. You will find a list of all the exemptions in Article 4 of the Covid-19 Ordinance on International Transport Measures. They include, for example:
- Business travellers who are travelling for an important reason that cannot be postponed.
- Individuals travelling for an important medical reason that cannot be postponed.
- Transit passengers who have spent less than 24 hours in a country or area with an increased risk of infection.
21.12.2020
Coronavirus: Entry ban and retroactive quarantine for persons from the UK and South Africa
Bern, 21.12.2020 - Following the discovery of a new, more contagious variant of the coronavirus in the UK and South Africa, the Federal Council today decided to take steps to prevent the further spread of this new virus strain. All persons who have entered Switzerland from these two countries since 14 December must go into quarantine for 10 days. The Federal Council has also introduced a general entry ban from today for all foreign nationals seeking to enter Switzerland from the UK and South Africa. This is intended in particular to stop travel from these countries for tourism purposes.
The Federal Council has approved amendments to COVID-19 Ordinance 3 prohibiting air travel between Switzerland and the UK and South Africa. The Federal Office of Civil Aviation FOCA yesterday ordered flights between Switzerland and these two countries to be suspended as of midnight on Sunday, 20 December.
A temporary derogation from the flight ban is being considered for persons resident in the UK or South Africa currently staying in Switzerland so that they may return home. That is also the case for persons resident in Switzerland currently staying in those two countries. However, it is imperative that such return journeys do not lead to infections.
The Federal Council also decided to withdraw freedom of movement privileges from persons resident in the UK until 31 December. Persons from the UK are therefore subject to a general ban on entering Switzerland. Freedom of movement privileges for British citizens were due to expire at the end of the year anyway.
The UK and South African authorities were given prior notice of the measures.
Initial indications are that the new variant of the coronavirus is significantly more transmissible than the existing strain. It is not yet clear to what extent the new strain has spread outside the UK and South Africa. No cases of the new strain have so far been identified in Switzerland.
Ordonnance 3 sur les mesures destinées à lutter contre le coronavirus (French)
List valid updon arriving in Switzerland from 28.12.2020
Areas of neighbouring countries
Germany:
- Land Sachsen
Italy:
- Region Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Region Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Belize
- Croatia
- Georgia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Montenegro
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovenia
- Sweden
- South Africa
- United Kingdom of Great Britain
- United States of America
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
19.12.2020
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland between 19.12.2020 and 27.12.2020
Areas of neighbouring countries
Italy:
- Region Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Region Veneto
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Croatia
- Georgia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Montenegro
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- United Kingdom of Great Britain
- United States of America
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
12.12.2020
List of countries and areas with an increased risk of infection
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold. No longer on the list from 14 december 2020: Czechia.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland from 14.12.2020
Areas of neighbouring countries
France:
- Overseas area French Polynesia
Italy:
- Region Emilia Romagna
- Region Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Region Veneto
Austria:
- Land Kärnten
- Land Salzburg
- Land Steiermark
- Land Upper Austria
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Croatia
- Georgia
- Hungary
- Jordan
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Montenegro
- North Macedonia
- Poland
- Portugal
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovenia
- United States of America
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
23.11.2020
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland between 23.11.2020 and 13.12.2020
No longer on the list since 23 November 2020: Armenia, Belgium, Region Hauts-de-France, Region Île de France.
Areas of neighbouring countries
France:
- Overseas area French Polynesia
Austria:
- Land Salzburg
- Land Upper Austria
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Czechia
- Luxemburg
- Montenegro
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland between 29.10.2020 and 22.11.2020
Areas of neighbouring countries
France:
- Region Hauts-de-France
- Region Île de France
- Overseas area French Polynesia
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Belgium
- Czech Republic
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland between 29.10.2020 and 22.11.2020
Areas of neighbouring countries
France:
- Region Hauts-de-France
- Region Île de France
- Overseas area French Polynesia
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Belgium
- Czech Republic
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately.
28.10.2020
People arriving in Switzerland from certain countries and areas are required to go into quarantine. The list of these countries and areas will be updated on 29 October 2020. A negative test does not exempt you from the mandatory quarantine requirement.
- Who must go into quarantine?
- Criteria for the list
- List of countries and areas
- What to do after entering Switzerland
- Information on quarantine
- Contact details for the cantonal authorities
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland from 29.10.2020
Areas of neighbouring countries
France:
- Region Hauts-de-France
- Region Île de France
- Overseas area French Polynesia
Countries and areas*
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Belgium
- Czech Republic
*The following applies for all countries that do not share a border with Switzerland: If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately
However, various people are exempt from the quarantine requirement in Switzerland. You will find a list of all the exemptions in Article 4 of the Covid-19 Ordinance on International Transport Measures. They include, for example:
- Business travellers who are travelling for an important reason that cannot be postponed.
- Individuals travelling for an important medical reason that cannot be postponed.
- Transit passengers who have spent less than 24 hours in a country or area with an increased risk of infection.
18.10.2020
Confederation imposes tougher measures to combat coronavirus
From Monday, 19 October spontaneous gatherings of more than 15 persons are not permitted in public. A mask must be worn in publicly accessible indoor areas, including in all railway stations and airports, and at bus and tram stops. Moreover, there are now new rules for private events of more than 15 persons, and in restaurants, bars and clubs food and drink may only be consumed sitting down. Following consultations with the cantons, the Federal Council has adapted the Special Situation COVID-19 Ordinance accordingly. This now also includes a recommendation to work from home.
The rapid rise in coronavirus cases in the last few days is a cause for great concern. The number of cases is on the increase in all age groups and across all cantons. The number of persons admitted to hospital is also rising. The new national measures agreed by the federal government and the cantons aim to better protect the public’s health and to prevent the health system from becoming overwhelmed in the coming weeks and months. The intention is also to considerably curb the number of new cases so that the cantons can continue to contract trace effectively. Despite the restrictions, it is hoped that the economy can continue to function and people can live their lives with as little disruption as possible.
Masks now mandatory in the whole of Switzerland
The requirement for persons over the age of 12 to wear a mask on public transport has been in place since 6 July. From Monday 19 October this will be extended to railway stations including platforms, airports and other publicly accessible public transport areas. As before, persons who are unable to wear a mask for medical reasons are exempt from the requirement.
Masks are now also compulsory in publicly accessible indoor spaces including all shops, shopping centres, banks, post offices, museums, libraries, cinemas, theatres, concert venues, indoor areas of zoos and botanical gardens, restaurants, bars, discos, casinos, hotels (with the exception of guests’ rooms), entrance areas and changing rooms in swimming pools, sports facilities and gyms, doctor’s surgeries, hospitals and places of worship, advisory centres and neighbourhood centres. Masks must also be worn in publicly accessible areas of administrative buildings.
Face masks must also be worn in all schools and higher education establishments, in child-care facilities and in the training areas of sport and fitness centres if part of the centre’s precautionary measures.
Rules for private events
Many people become infected with the coronavirus when families and friends gather. Gatherings should be avoided were possible. At private events attended by over 15 people, food and drink may only be consumed while seated. Anyone standing up must wear a mask. Furthermore, hygiene rules must be observed at all times and contact details must be recorded. For private events of more than 100 people there must be a set of precautionary measures (as for public events) and may only be held in publicly accessible venues.
Gatherings of more than 15 not permitted in public
Spontaneous gatherings of more than 15 persons are not permitted in public spaces such as town squares, streets, paths and parks. The aim is to prevent private events moving outdoors. Organised outdoor events such as political and civil society demonstrations are permitted provided precautionary measures are observed.
Seating requirement in bars, clubs and restaurants
In restaurants, bars and clubs, food and drink may only be consumed while seated, both indoors and out.
Working from home recommended
The Federal Council has added a paragraph on working from home to the Special Situation COVID-19 Ordinance. Employers are now required to observe the recommendation by the Federal Office of Public Health for employees to work from home. This will prevent large numbers of people coming together, particularly at peak times, and reduce close contact in the workplace. It will also reduce the risk of a whole work team having to go into quarantine if one member becomes infected with COVID-19.
Since 19 June, the cantons have played the lead role in combating the COVID-19 epidemic in Switzerland. The Confederation still expects the cantons to conduct widespread testing, implement a sound system of contract tracing and employ targeted measures to help fight the epidemic.
Further information: https://www.bag.admin.ch/bag/en/home/das-bag/aktuell/news/news-18-10-2020.html
09.10.2020
No longer on the list from 12 October 2020: Bolivia, Dominican Republic, Namibia, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago.
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland from 12.10.2020
Areas of neighbouring countries
Germany:
- Land Berlin
- Land Hamburg
France:
- Region Bretagne
- Region Centre-Val de Loire
- Region Corse
- Region Hauts-de-France
- Region Île de France
- Region Normandie
- Region Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Region Occitanie
- Region Pays de la Loire
- Region Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
- Overseas area French Guyana
- Overseas area French Polynesia
- Overseas area Guadeloupe
- Overseas area La Réunion
- Overseas area Martinique
- Overseas area Mayotte
- Overseas area Saint-Barthélemy
- Overseas area Saint-Martin
Italy:
- Region Campania
- Region Liguria
- Region Sardinia
- Region Veneto
Austria:
- Land Burgenland
- Land Lower Austria
- Land Salzburg
- Land Upper Austria
- Land Vienna
Countries and areas
- Albania
- Andorra
- Argentina
- Armenia
- The Bahamas
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Belize
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brazil
- Canada
- Cape Verde
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Croatia
- Czech Republic
- Kingdom of Denmark
- Ecuador
- Georgia
- Guyana
- Honduras
- Hungary
- Iceland
- India
- Iran
- Iraq
- Ireland
- Israel
- Jamaica
- Jordan
- Kuwait
- Lebanon
- Libya
- Luxemburg
- Maldives
- Malta
- Morocco
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Nepal
- Kingdom of the Netherlands
- North Macedonia
- Occupied Palestinian Territory
- Oman
- Panama
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Portugal
- Qatar
- Romania
- Russia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Tunisia
- Ukraine
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom of Great Britain
- United States of America
30.09.2020
Entering Switzerland
Infoline for people travelling to Switzerland: +41 58 464 44 88 (6am–11pm)
Mandatory quarantine for persons arriving in Switzerland
Since 6 July 2020, anyone entering Switzerland from a country or area with a high risk of infection has been legally mandated to go into quarantine for ten days. You will find the list of these countries and further information on the page Mandatory quarantine for persons arriving in Switzerland.
Collection of contact details upon arriving in Switzerland
In some cases, the contact details of travellers will be collected upon their arrival in Switzerland. The collection of contact details affects all airline passengers as well as coach passengers from countries with an increased risk of infection.
There are two reasons for the collection of contact details: on the one hand, this guarantees traceability in the event that there were infectious passengers on board and a transmission of the new coronavirus is possible. On the other, the contact details are used by the cantonal authorities in order to monitor compliance with mandatory quarantine through spot checks.
Contact details of the responsible cantonal authorities
Contact your local cantonal authority within two days of your arrival.
| Canton | Contact details |
|---|---|
| Aargau | Online application form (In German) |
| Appenzell Ausserrhoden | Online application form (In German) |
| Appenzell Innerrhoden | Homepage (In German) |
| Basel-Landschaft | Homepage (In German) |
| Basel-Stadt | Homepage (In German) |
| Bern | Online application form (In German) |
| Fribourg | Homepage (In German) |
| Geneva | Online application form (In French) |
| Glarus | +41 55 646 61 40 |
| Graubünden | |
| Jura | +41 32 420 99 00 |
| Lucerne | Homepage (In German) |
| Neuchâtel | +41 32 889 11 00 |
| Nidwalden | Homepage (In German) |
| Obwalden | |
| St. Gallen | Online application form (In German) |
| Schaffhausen | +41 52 632 70 01 |
| Schwyz | Homepage (In German) |
| Solothurn | Homepage (In German) |
| Thurgau | +41 58 345 34 40 |
| Ticino | Online application form |
| Uri | +41 41 874 34 33 |
| Valais | +41 58 433 01 44 |
| Vaud | Online application form (in French) |
| Zug | +41 41 728 39 09 |
| Zurich | Online application form |
| Principality of Liechtenstein | Homepage (in German) |
25.09.2020
Mandatory quarantine for persons arriving in Switzerland
List of countries and areas
The countries and areas with a high risk of infection are set down in the Covid-19 Ordinance on International Passenger Transport Measures
If a country is on the list, this includes all of its areas, islands and overseas territories – even if they are not listed separately. Switzerland’s neighbouring countries are exempted from this regulation. In the case of these countries, it is not the entire country that is listed, but rather regions. Further information in this regard can be found on the page Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs).
No longer on the list from 28 September 2020: Kosovo, San Marino.
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland from 28.9.2020
Areas of neighbouring countries
France:
- Region Bretagne
- Region Centre-Val de Loire
- Region Corse
- Region Hauts-de-France
- Region Île de France
- Region Normandie
- Region Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Region Occitanie
- Region Pays de la Loire
- Region Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
- Overseas area French Guyana
- Overseas area French Polynesia
- Overseas area Guadeloupe
- Overseas area La Réunion
- Overseas area Martinique
- Overseas area Mayotte
- Overseas area Saint-Barthélemy
- Overseas area Saint-Martin
Italy:
- Region Liguria
Austria:
- Land Lower Austria
- Land Upper Austria
- Land Vienna
Countries and areas
- Albania
- Andorra
- Argentina
- Armenia
- The Bahamas
- Bahrain
- Belgium
- Belize
- Bolivia
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brazil
- Cape Verde
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Croatia
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Dominican Republic
- Ecuador
- Guyana
- Honduras
- Hungary
- Iceland
- India
- Iraq
- Ireland
- Israel
- Jamaica
- Kuwait
- Lebanon
- Libya
- Luxemburg
- Maldives
- Malta
- Morocco
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Namibia
- Nepal
- Netherlands
- North Macedonia
- Occupied Palestinian Territory
- Oman
- Panama
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Portugal
- Qatar
- Romania
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Suriname
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Ukraine
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom of Great Britain
- United States of America
What to do after entering Switzerland
- Upon arrival, go immediately to your home or to other suitable accommodation (e.g. a hotel or holiday apartment). On the way there, keep a minimum distance of 1.5 metres from other people. If you are unable to maintain this distance, we recommend that you wear a mask. Avoid public transport if possible.
- Report your arrival to the cantonal authority responsible within two days. Follow the instructions of the cantonal authority.
- For 10 days after your arrival in Switzerland you must stay in your home or other suitable accommodation without going out. Avoid contact with other people and follow the instructions on quarantine (PDF, 182 kB, 12.09.2020).
Anyone who fails to comply with the quarantine requirement or the duty to report to the authorities is committing an offence under the Epidemics Act (in German), which can be punished by a fine of up to CHF 10,000.
The document ‘Instructions on quarantine’ can be found in various languages on our website Downloads in various languages.
Information on quarantine
Anyone who may have become infected with the new coronavirus must go into quarantine. If they fall ill they should avoid all contact with other people in order to prevent the spread of the virus. The quarantined person should stay at home or in some other suitable accommodation and not leave for any reason.
Who has to go into quarantine and how long must they stay there? What should you do if you are in quarantine and live with other people? This and other information can be found in the document Instructions on quarantine (PDF, 182 kB, 12.09.2020).
Children
Children entering Switzerland from a country or area mentioned on the list must also spend 10 days in quarantine.
11.09.2020
Mandatory quarantine: list of countries and areas
The countries and areas with a high risk of infection are set down in the Covid-19 Ordinance on International Passenger Transport Measures. This list is regularly updated.
No longer on the list from 14 September 2020: Ecuador, Faroe Islands, Guatemala, South Africa.
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold.
Information regarding Spain: the Canary Islands will be included on the list from 14 September, meaning that the whole of Spain is now on the list.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland from 14.9.2020
List of countries and areas with a high risk of infection
List of countries and areas with a high risk of infection
- Albania
- Andorra
- Argentina
- Armenia
- Aruba
- The Bahamas
- Bahrain
- Belize
- Bolivia
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brazil
- British Virgin Islands
- Cape Verde
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Croatia
- Czech Republic
- Dominican Republic
- Gibraltar
- Guyana
- Honduras
- India
- Iraq
- Israel
- Kosovo
- Kuwait
- Lebanon
- Libya
- Maldives
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Namibia
- North Macedonia
- Occupied Palestinian Territory
- Panama
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Qatar
- Romania
- San Marino
- Sint Maarten
- Spain
- Suriname
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- Ukraine
- United Arab Emirates
- United States of America (including Puerto Rico, US Virgin Islands and Guam)
List of areas of neighbouring countries with a high risk of infection
Areas in France:
- Region Centre-Val de Loire
- Region Corse
- Region Hauts-de-France
- Region Île de France
- Region Normandie
- Region Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Region Occitanie
- Region Pays de la Loire
- Region Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
- Overseas area French Guyana
- Overseas area Guadeloupe
- Overseas area French Polynesia
- Overseas area La Réunion
- Overseas area Martinique
- Overseas area Mayotte
- Oversesas area Saint-Barthélemy
- Overseas area Saint-Martin
Areas in Austria:
- Federal state Vienna
At its meeting on 11 September, the Federal Council decided on the quarantine rules for persons entering Switzerland from neighbouring countries: only those regions of neighbouring countries where the infection rate is over the limit will be added to the list of countries and areas with an increased rate of infection, not the entire country. Border regions may be exempted from inclusion on the list. In so doing, the Federal Council is responding to the rapid rise in infection numbers, while still taking account of the close interaction between Switzerland and neighbouring regions. The revised ordinance will come into force on 14 September. At the same time, the list of risk areas will be updated.
Since 6 July, anyone entering Switzerland from a country or area with a high risk of infection has been required to go into quarantine for ten days. This Federal Council measure aims to prevent the import of the coronavirus into Switzerland and its spread within the country as far as possible. The Federal Council is now taking a region-based approach to neighbouring countries. Only specific regions of neighbouring countries will be included in the list of countries and areas with an increased risk of infection, in line with the practice in various other countries.
Exemptions for border regions
The border regions of neighbouring countries may be exempted from inclusion on the list. By allowing this exception, the Federal Council is taking account of the close economic, social and cultural exchanges that take place in the border regions. At the same time, the Federal Council is responding to the increasing numbers of infections in Switzerland and in various neighbouring countries, particularly in France.
Since June, the number of new infections in Switzerland has been rising steadily. While 98 cases were reported in the first week of June, at the end of August the figure was 1844, i.e. 18-times higher. In France, the number of cases is increasing even more rapidly and the number of new infections over two weeks in almost all regions of France is considerably higher than the limit value of 60 per 100,000 persons (14-day incidence). In certain Austrian states, a rise in cases in excess of the threshold has also been recorded, as it has in several Swiss cantons.
Taking a regional approach means that persons returning to Switzerland from risk areas will be required to go into quarantine, but not persons returning from regions on the Swiss border. In implementing this measure, the Federal Council is continuing to rely on members of the public to act responsibly. They should avoid travelling to risk areas if at all possible, or spend time in quarantine if they have travelled to these regions. Cross-border commuters are already exempted from the quarantine requirement.
The majority of cantons have expressed their support for this approach. However, some cantons are concerned that the new exemptions for the border regions will lead to increased costs and may lead to lower levels of compliance with the quarantine rules.
Exemptions from the quarantine requirement
Under the new rules, creative artists returning from a cultural event, athletes returning from competitions and persons who have been attending professional conferences will be exempted from the quarantine requirement. However, this exemption only applies if precautionary measures have been planned and taken at the foreign event concerned.
Also exempted from the quarantine requirement are persons who are required to travel without delay to a risk area for professional or medical reasons. The persons concerned must not remain abroad for more than five days, and precautionary measures must be planned and taken.
In addition, the Federal Council has revised the calculation rules for quarantine in the COVID-19 Ordinance on International Passenger Transport Measures. This will allow the cantons to take account of time spent in a country where there is not a high risk of infection before entering Switzerland, and to reduce the length of time spent in quarantine in Switzerland accordingly.
Coronavirus tests: Federal government reduces tariffs
At its meeting, the Federal Council also decided to reduce the tariff for a molecular-biological analysis for Sars-CoV-2 (PCR test) from CHF 95 to CHF 82 and that for a serological analysis (antibody test) from CHF 39 to CHF 25. It has also specified the details of various procedures.
Further information: Ordonnance sur les mesures destinées à lutter contre le coronavirus dans le domaine du transport international de voyageurs (PDF, 399 kB)
_______________________________________________________________________
07.09.2020
Mandatory quarantine: updated list of countries and areas
No longer on the list since 7 September 2020: Belgium, El Salvador, Eswatini (Swazsiland), Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Luxembourg, Mexico, Oman.
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland from 7.9.2020
Important: a negative test result does not exempt you from the mandatory quarantine requirement or shorten the quarantine period. This is because a negative test result does not rule out an infection with the new coronavirus. You will find the biological explanation for this on the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) page.
The mandatory quarantine requirement does not apply to transit passengers who have spent less than 24 hours in a country or area with an increased risk of infection. Further exceptions are set down in Article 4 of the Covid-19 Ordinance on International Passenger Transport Measures.
Anyone who fails to comply with the quarantine requirement or the duty to report to the authorities is committing an offence under the Epidemics Act (in German), which can be punished by a fine of up to CHF 10,000.
_______________________________________________________________________
18.08.2020
Mandatory quarantine: updated list of countries and areas
The countries and areas with a high risk of infection are set down in the Covid-19 Ordinance on International Passenger Transport Measures. This list is regularly updated.
Removed from the list on 20 August 2020: Equatorial Guinea, São Tomé and Príncipe, Saudi Arabia, Serbia and Singapore
The newly added countries and areas are written in bold.
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland from 20 August 2020
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland between 8 August 2020 and 19 August 2020
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland between 23 July 2020 and 7 August 2020
List valid upon arriving in Switzerland between 6 July 2020 and 22 July 2020
Source: https://www.bag.admin.ch/.........
https://reopen.europa.eu/en/map/CHE
_____________________________________________________________
14.08.2020
Travelling to Switzerland
Travelling from EU/EAA countries, including the United Kingdom, is in principle allowed.
All travellers entering Switzerland from countries or regions that are defined as Covid risk areas will have to quarantine for 10 days. The Federal Office of Public Health keeps a list of countries concerned, which is updated regularly.
As of 8.8.20, Luxembourg, Romania and Spain (with the exception of the Balearic and Canary Islands) are defined as Covid risk areas.
Travelling from Switzerland or returning to Switzerland
From the beginning of the pandemic, the Swiss Government has been advising against non-urgent travel abroad. This advice has gradually been lifted for a selection of countries.
Currently, the following countries are exempt from the general advice against non-urgent travel abroad: countries in the Schengen area, United Kingdom, Andorra, Australia, Bulgaria, Canada, Croatia, Cyprus, Georgia, Ireland, Japan, Morocco, Monaco, New Zealand, Romania, Rwanda, San Marino, South Korea, Thailand, Tunisia, Urugay, Vatican/Holy See.
If you re-enter Switzerland having at any point in the past 14 days spent time in a state or area defined as a Covid risk area, you must immediately go to your home or to other suitable accommodation, where you must stay for 10 days from the day of your arrival. Also, you have to report your arrival to the responsible cantonal authority within two days, and follow its instructions. The list of countries and territories with increased covid-infection risks is defined and regularly updated in a Federal Act.
Following the EU council recommendations, entry restrictions are lifted for a selection of third countries. It currently concerns: Australia, Canada, Georgia, Japan, Morocco, New Zealand, Rwanda, South Korea, Thailand, Tunesia, and Urugay, and the EU states outside the Schengen area (Bulgaria, Ireland, Croatia, Romania, and Cyprus). China is also expected to be removed from the list in line with the EU recommendations, provided it guarantees reciprocal rights of entry to people travelling from Switzerland.
An updated list of States and areas with an increased risk of infection is available at www.bag.admin.ch
Rules and Exceptions
Entry restrictions have been lifted for residents of EU/EEA countries (including UK), as well as for their family members (irrespective of their nationality).
Travellers that are required to go into quarantine willl be notified during the flight, on board of coaches and at border crossings. They will have to register with the cantonal authorities within two days after arrival, and follow their instructions. Airline and travel companies will be instructed not to transport sick passengers.
For updated information, also see the State Secretariat for Migration (SEM) FAQs
Links to national sources
www.bag.admin.ch
Source: Driving abroad
https://reopen.europa.eu/en/map/CHE
Source: Federal Office of Transport FOT
30.06.2020
Country | General | Land | Aviation | |
Switzerland |
|
|
|
Travel ban to Switzerland from Italy, Germany, France and Austria
End date: not available
Further information: https://www.bag.admin.ch/bag/de/home/krankheiten/ausbrueche-epidemien-pa...